Manufacturing Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production
Manufacturing Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Manufacturing Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Manufacturing Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production

The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and a global shift towards sustainability. As we approach 2025, several key trends are shaping the future of production, offering both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers.
Understanding the Forces Driving Change
Several factors are driving the evolution of manufacturing:
- Technological Advancements: The rapid development of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) is enabling manufacturers to automate processes, optimize production, and improve efficiency.
- Globalization and Supply Chain Disruptions: The interconnectedness of global supply chains has exposed vulnerabilities, leading to a focus on reshoring, regionalization, and building more resilient supply networks.
- Consumer Demand for Customization and Personalization: Consumers increasingly demand products tailored to their specific needs and preferences, driving the need for flexible and responsive manufacturing processes.
- Sustainability and Environmental Concerns: Growing environmental awareness and regulations are pushing manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices, reduce waste, and minimize their environmental impact.
Key Manufacturing Trends Shaping 2025
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in Manufacturing: AI and ML are transforming manufacturing by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and optimizing processes.
- Applications: AI-powered predictive maintenance can anticipate equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to optimize production schedules, identify bottlenecks, and improve resource allocation.
- Benefits: Increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved product quality, and enhanced decision-making.
- Challenges: Data security, ethical considerations, and the need for skilled personnel to implement and manage AI systems.
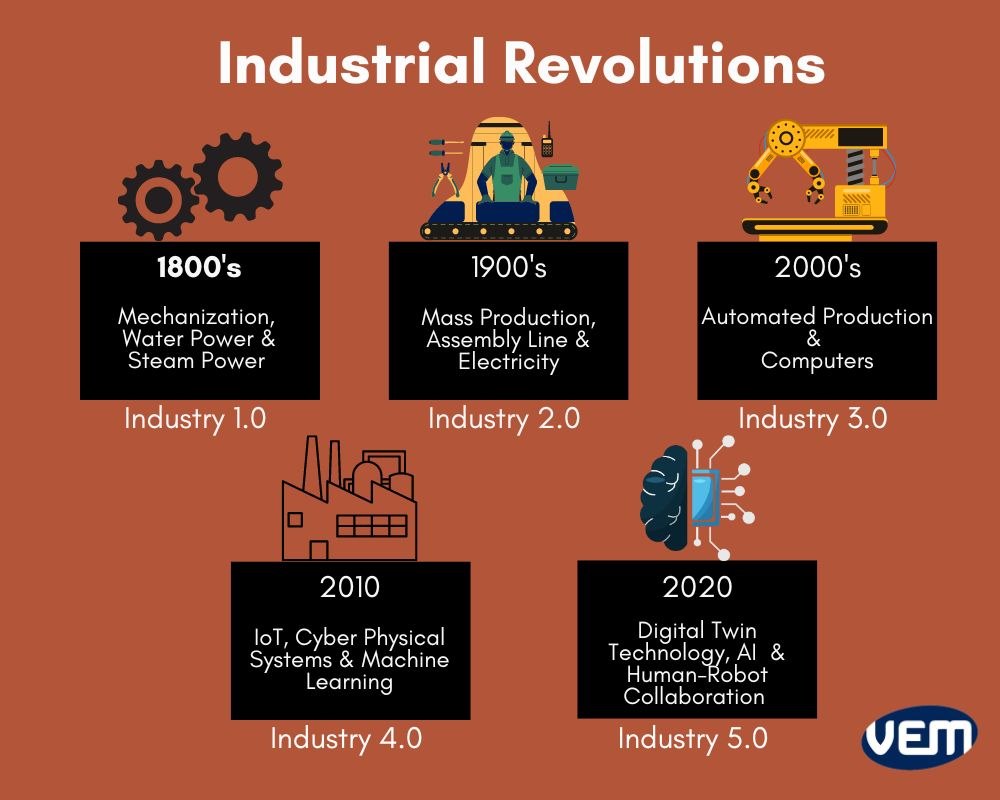
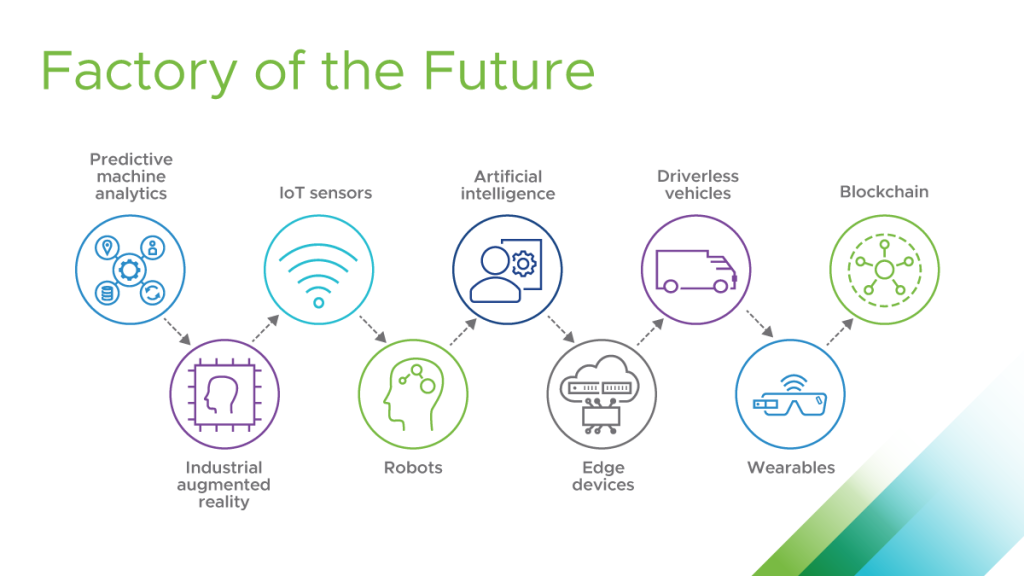
2. Industry 4.0 and the Smart Factory: The concept of Industry 4.0 encompasses the integration of digital technologies, such as AI, IoT, and cloud computing, to create interconnected and intelligent manufacturing systems.
- Smart Factory Features: Real-time data collection and analysis, automated production processes, predictive maintenance, and connected supply chains.
- Benefits: Enhanced productivity, improved quality control, increased flexibility, and reduced waste.
- Challenges: High upfront investment costs, cybersecurity concerns, and the need for workforce training to adapt to new technologies.
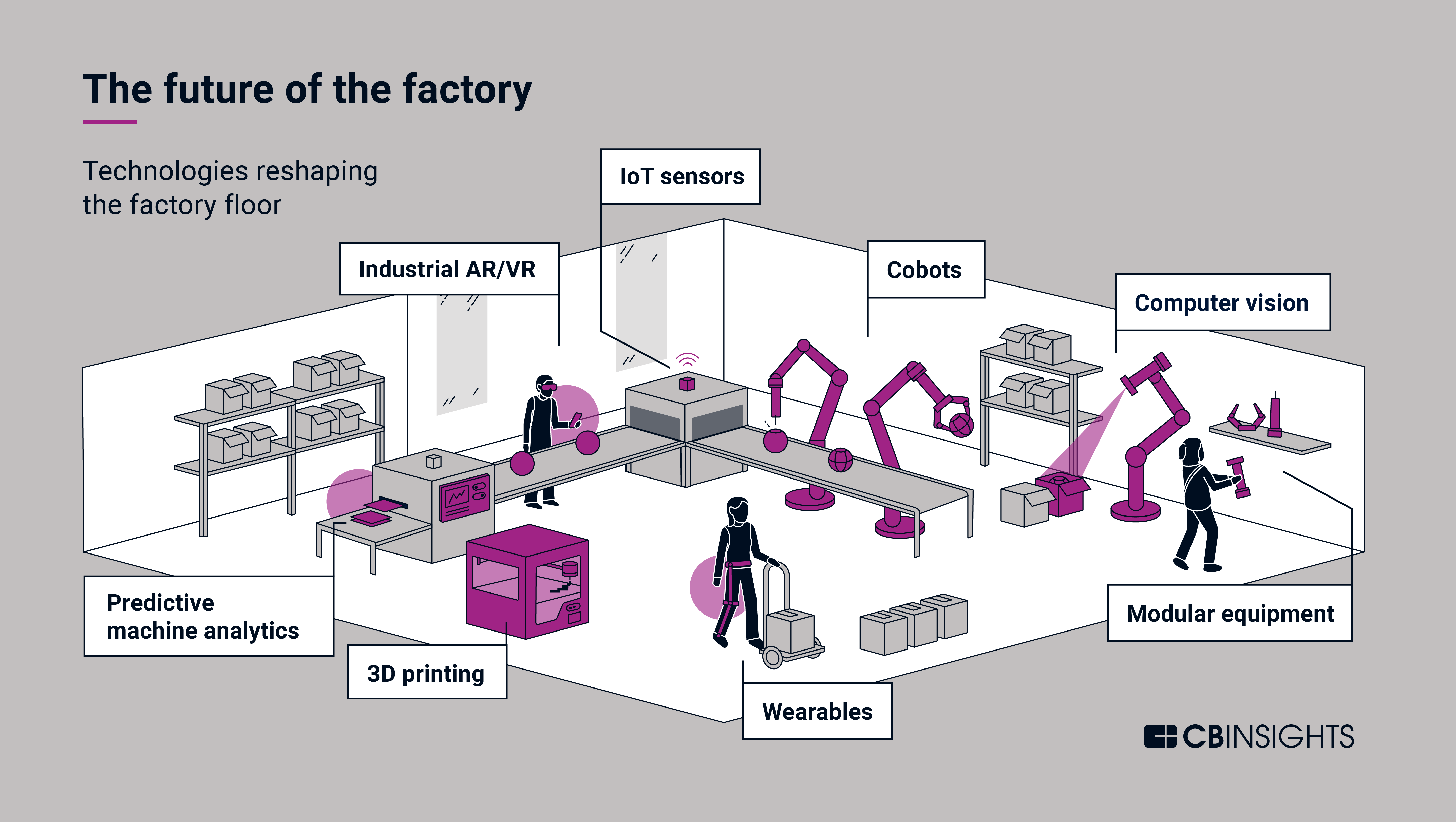
3. Robotics and Automation: Robotics and automation are becoming increasingly prevalent in manufacturing, automating repetitive and hazardous tasks, improving efficiency, and enhancing safety.
- Types of Robots: Collaborative robots (cobots) designed to work alongside humans, industrial robots for heavy-duty tasks, and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) for material handling.
- Benefits: Increased productivity, reduced labor costs, improved safety, and enhanced product quality.
- Challenges: High initial investment costs, potential job displacement, and the need for skilled personnel to operate and maintain robots.
4. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Additive manufacturing allows manufacturers to create complex parts and products layer by layer, enabling greater design freedom, customization, and on-demand production.
- Applications: Prototyping, tooling, customized products, and the production of complex geometries.
- Benefits: Reduced lead times, lower tooling costs, greater design flexibility, and the ability to produce customized products on demand.
- Challenges: Limited material options, scalability challenges, and the need for specialized expertise.
5. Sustainable Manufacturing: Manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices to reduce their environmental impact, conserve resources, and meet evolving regulations.
- Sustainable Practices: Energy efficiency, waste reduction, water conservation, and the use of recycled materials.
- Benefits: Reduced environmental impact, cost savings, and improved brand reputation.
- Challenges: Implementing sustainable practices can require significant investments and changes to existing processes.
6. Cloud Computing and Data Analytics: Cloud computing enables manufacturers to access and process vast amounts of data, while data analytics provides insights to optimize operations, improve decision-making, and enhance efficiency.
- Cloud-based Manufacturing Applications: Production planning, inventory management, supply chain optimization, and quality control.
- Benefits: Improved scalability, cost savings, enhanced collaboration, and real-time data access.
- Challenges: Data security concerns, the need for robust internet connectivity, and the requirement for data management expertise.
7. The Rise of the Digital Twin: A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical asset, enabling manufacturers to simulate and optimize processes, predict performance, and identify potential issues before they occur.
- Applications: Product design, process optimization, predictive maintenance, and virtual commissioning.
- Benefits: Reduced downtime, improved efficiency, enhanced product quality, and reduced risk.
- Challenges: Data collection and integration, model development and validation, and the need for specialized expertise.
8. The Workforce of the Future: The evolving manufacturing landscape requires a workforce with new skills and capabilities, including digital literacy, problem-solving abilities, and adaptability.
- Skills in Demand: Data analysis, programming, robotics operation, and AI/ML expertise.
- Benefits: Improved productivity, innovation, and competitiveness.
- Challenges: Bridging the skills gap, attracting and retaining talent, and providing ongoing training and development opportunities.
Related Searches
1. Future of Manufacturing: Exploring the long-term trends and technological advancements shaping the manufacturing industry.
2. Manufacturing Automation Trends: Focusing on the increasing adoption of robotics, AI, and other automation technologies in manufacturing.
3. Digital Transformation in Manufacturing: Examining the impact of digital technologies, such as Industry 4.0, on manufacturing processes and business models.
4. Sustainable Manufacturing Practices: Highlighting the importance of environmental sustainability and the adoption of green manufacturing practices.
5. Manufacturing Industry 4.0: Delving into the specific technologies and applications of Industry 4.0 in the manufacturing sector.
6. Manufacturing Technology Trends: Analyzing the latest advancements in manufacturing technologies, including AI, robotics, and additive manufacturing.
7. Manufacturing Skills Gap: Addressing the challenge of finding and training skilled workers for the evolving manufacturing industry.
8. Manufacturing Innovation: Exploring the role of innovation in driving growth and competitiveness in the manufacturing sector.
FAQs about Manufacturing Trends 2025
1. What are the major benefits of adopting these manufacturing trends?
Adopting these trends can lead to increased efficiency, productivity, and profitability. Manufacturers can improve product quality, reduce costs, and enhance their competitiveness in the global marketplace. Additionally, embracing sustainability practices helps reduce environmental impact and fosters a positive brand image.
2. What are the biggest challenges associated with these trends?
The primary challenges include high upfront investment costs, the need for skilled personnel, cybersecurity concerns, and the potential for job displacement. Manufacturers need to carefully assess the risks and benefits of adopting these trends and develop strategies to mitigate potential challenges.
3. How can manufacturers prepare for these trends?
Manufacturers can prepare by investing in training and development programs to equip their workforce with the necessary skills. They should also explore partnerships with technology providers and research institutions to stay abreast of the latest advancements. Furthermore, embracing a culture of innovation and continuous improvement is crucial for adapting to the evolving manufacturing landscape.
4. What are the long-term implications of these trends?
These trends are expected to reshape the manufacturing industry, leading to increased automation, greater customization, and a shift towards sustainable practices. They will also drive the demand for a skilled workforce with expertise in digital technologies and data analysis.
Tips for Manufacturers in 2025
- Embrace a culture of innovation: Continuously explore new technologies and processes to maintain a competitive edge.
- Invest in workforce development: Train employees in digital skills and emerging technologies to adapt to the changing landscape.
- Prioritize data security: Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and intellectual property.
- Foster collaboration: Partner with technology providers, research institutions, and other manufacturers to share knowledge and accelerate innovation.
- Embrace sustainability: Adopt sustainable practices to reduce environmental impact and enhance brand reputation.
Conclusion
The manufacturing trends of 2025 present both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers. By embracing innovation, investing in technology and workforce development, and prioritizing sustainability, manufacturers can position themselves for success in the evolving global marketplace. The future of manufacturing is bright, driven by technological advancements and a commitment to creating a more sustainable and efficient production system.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Manufacturing Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Production. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!