Navigating the Future of Food: Health Trends Shaping 2025
Navigating the Future of Food: Health Trends Shaping 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Future of Food: Health Trends Shaping 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Future of Food: Health Trends Shaping 2025
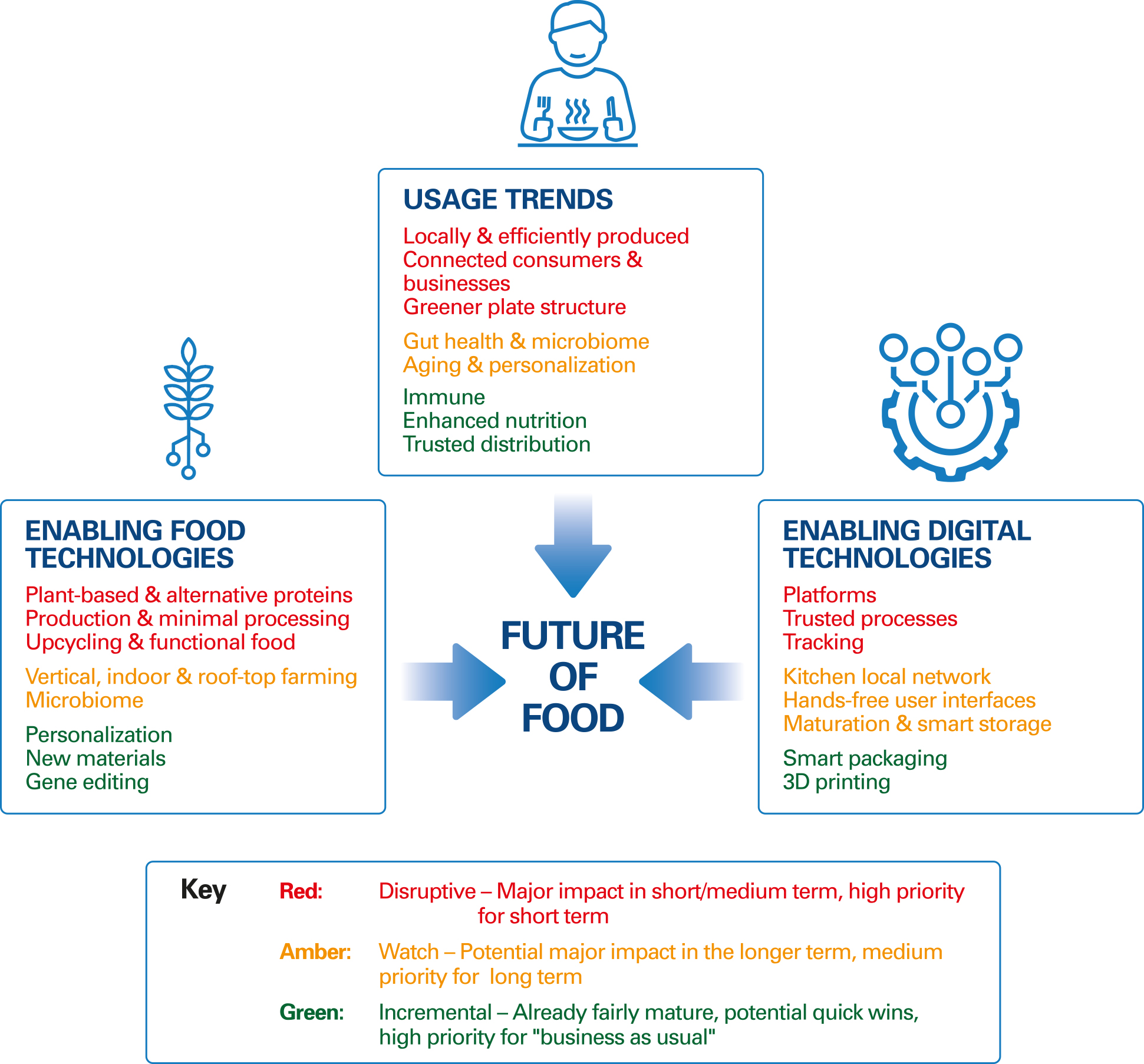
The landscape of food consumption is in constant flux, driven by evolving consumer preferences, scientific advancements, and a growing awareness of the interconnectedness between food and well-being. As we approach 2025, several key trends are poised to reshape how we eat, interact with food, and prioritize health. Understanding these trends is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike, as they offer insights into the future of food and its impact on our lives.
Food Health Trends 2025
1. Personalized Nutrition: The era of one-size-fits-all nutrition is waning. Personalized nutrition, powered by advancements in genomics, microbiome analysis, and artificial intelligence, is gaining momentum. This approach tailors dietary recommendations to individual needs and preferences, considering factors like genetics, gut health, and lifestyle.
Benefits:
- Improved health outcomes: Personalized nutrition plans can help individuals achieve specific health goals, such as weight management, disease prevention, or optimized performance.
- Increased adherence: Tailored recommendations are more likely to resonate with individuals, leading to better compliance and long-term success.
- Empowerment: Individuals gain greater control over their health and well-being through personalized insights.
2. Plant-Based Foods: The demand for plant-based foods continues to surge, fueled by concerns about animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and personal health. This trend encompasses a wide range of products, from plant-based meats and dairy alternatives to innovative plant-based ingredients.
Benefits:
- Reduced environmental impact: Plant-based diets typically have a lower carbon footprint compared to meat-heavy diets.
- Improved health: Plant-based foods are often rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, promoting overall well-being.
- Increased accessibility: The growing variety of plant-based products makes it easier for individuals to adopt a more plant-centric lifestyle.
3. Functional Foods and Ingredients: The focus on food as a vehicle for health goes beyond basic nutrition. Functional foods and ingredients, enriched with specific bioactive compounds, target specific health concerns. Examples include foods fortified with probiotics for gut health, omega-3 fatty acids for brain function, or antioxidants for immune support.
Benefits:
- Targeted health benefits: Functional foods can address specific health needs and potentially mitigate the risk of chronic diseases.
- Convenience: Integrating functional ingredients into everyday foods offers a convenient way to enhance dietary intake.
- Proactive health management: Functional foods empower individuals to take a proactive approach to their health.
4. Sustainable Food Systems: The future of food is intricately linked to sustainability. Consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental and social impacts of their food choices. This trend encourages responsible agricultural practices, reduced food waste, and localized food production.
Benefits:
- Preservation of natural resources: Sustainable food systems aim to minimize resource depletion and environmental degradation.
- Support for local communities: Localized food production strengthens local economies and promotes food security.
- Ethical food choices: Consumers can align their food choices with their values, supporting ethical and sustainable practices.
5. Food Transparency and Traceability: Consumers are demanding greater transparency regarding the origins, production methods, and ingredients of their food. Traceability technologies are emerging to provide detailed information about the journey of food from farm to table.
Benefits:
- Informed decision-making: Consumers can make informed choices based on the information provided about food products.
- Enhanced food safety: Traceability systems can help track potential foodborne outbreaks and ensure food safety.
- Increased trust: Transparency fosters trust between consumers and food producers.
6. Food Waste Reduction: Reducing food waste is a critical aspect of sustainable food systems. Consumers, businesses, and governments are actively seeking solutions to minimize food waste at all stages of the food supply chain.
Benefits:
- Environmental protection: Food waste contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion.
- Food security: Reducing food waste helps ensure food availability for all.
- Cost savings: Reducing food waste translates into economic benefits for businesses and consumers.
7. Food Technology Innovations: Advancements in food technology are revolutionizing the way food is produced, processed, and consumed. Innovations include precision fermentation, vertical farming, and 3D food printing, which offer potential solutions to food security, sustainability, and nutritional challenges.
Benefits:
- Increased food production: Innovative technologies can help address food shortages and enhance food security.
- Reduced environmental impact: Some technologies, like vertical farming, offer a more sustainable approach to food production.
- Enhanced nutritional value: Food technology can enable the creation of novel foods with improved nutritional profiles.
8. Food as Medicine: The concept of "food as medicine" is gaining recognition, emphasizing the role of diet in disease prevention and management. This trend encourages the use of food as a therapeutic tool to support overall health and well-being.
Benefits:
- Disease prevention: A healthy diet can play a significant role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Improved health outcomes: Dietary interventions can help manage existing health conditions.
- Personalized approach: Food as medicine recognizes the individual nature of health and dietary needs.
Exploring Related Searches:
1. Future of Food Trends: This search explores broader trends shaping the future of food, including technological advancements, consumer preferences, and global challenges.
2. Food Industry Trends: This search focuses on trends specifically impacting the food industry, such as emerging technologies, consumer demands, and market shifts.
3. Food Sustainability Trends: This search examines trends related to sustainable food production, consumption, and waste management, highlighting the environmental and social impact of food choices.
4. Food Health Trends 2025: This search delves into specific health-focused trends anticipated to emerge by 2025, including personalized nutrition, plant-based diets, and functional foods.
5. Global Food Trends: This search examines global food trends, considering cultural differences, economic factors, and regional variations in food consumption patterns.
6. Food Technology Trends: This search explores advancements in food technology, such as precision fermentation, vertical farming, and 3D food printing, and their implications for the future of food.
7. Food Safety Trends: This search investigates emerging trends related to food safety, including traceability technologies, foodborne illness prevention, and regulatory changes.
8. Food Innovation Trends: This search focuses on innovative food products, concepts, and technologies, highlighting emerging trends in food development and consumer preferences.
FAQs:
1. What is personalized nutrition, and how does it work?
Personalized nutrition is a tailored approach to dietary recommendations based on individual factors like genetics, microbiome, and lifestyle. It uses data analysis and algorithms to create customized plans for optimal health outcomes.
2. What are the benefits of a plant-based diet?
Plant-based diets are typically associated with lower carbon footprints, improved gut health, reduced risk of chronic diseases, and increased intake of vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
3. How do functional foods contribute to health?
Functional foods are enriched with specific bioactive compounds that target specific health concerns, such as promoting gut health, boosting immunity, or improving brain function.
4. What are some examples of sustainable food practices?
Sustainable food practices include reducing food waste, supporting local farmers, choosing organic products, and opting for plant-based options.
5. How can food traceability improve food safety?
Traceability systems allow for tracking food products from farm to table, enabling faster identification of foodborne outbreaks and preventing wider contamination.
6. What are some examples of food technology innovations?
Food technology innovations include precision fermentation for creating meat alternatives, vertical farming for efficient food production, and 3D food printing for personalized and customized food creations.
7. How does the concept of "food as medicine" differ from traditional nutrition?
"Food as medicine" emphasizes the therapeutic potential of food in preventing and managing diseases, going beyond basic nutritional needs and recognizing the role of diet in overall health.
8. What are some key challenges and opportunities related to food health trends in 2025?
Challenges include ensuring equitable access to personalized nutrition, addressing ethical concerns surrounding food technology, and mitigating the impact of climate change on food systems. Opportunities lie in developing innovative solutions, fostering collaboration between stakeholders, and promoting consumer education.
Tips for Navigating Food Health Trends in 2025:
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of emerging trends and research findings related to food and health.
- Embrace personalization: Explore personalized nutrition options and consider genetic testing or microbiome analysis to tailor your diet.
- Prioritize plant-based foods: Incorporate more plant-based options into your diet, exploring diverse ingredients and recipes.
- Seek out functional foods: Look for foods enriched with specific bioactive compounds to address your individual health needs.
- Support sustainable food systems: Make conscious choices to reduce food waste, support local farmers, and opt for sustainable products.
- Demand transparency: Choose food products with clear labeling and traceable origins.
- Explore food technology: Stay informed about advancements in food technology and consider incorporating innovative options into your diet.
- View food as medicine: Recognize the therapeutic potential of food and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized dietary advice.
Conclusion:
The future of food is marked by a dynamic interplay of consumer preferences, technological advancements, and a growing awareness of the link between food and health. As we navigate the landscape of Food Health Trends 2025, embracing personalized nutrition, prioritizing plant-based choices, and adopting sustainable practices will be crucial for individual well-being and a healthier planet. By staying informed, making conscious choices, and embracing innovation, we can shape a future where food nourishes both our bodies and our world.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Future of Food: Health Trends Shaping 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!