Shaping the Future: Building Trends for 2025 and Beyond
Shaping the Future: Building Trends for 2025 and Beyond
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future: Building Trends for 2025 and Beyond. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shaping the Future: Building Trends for 2025 and Beyond
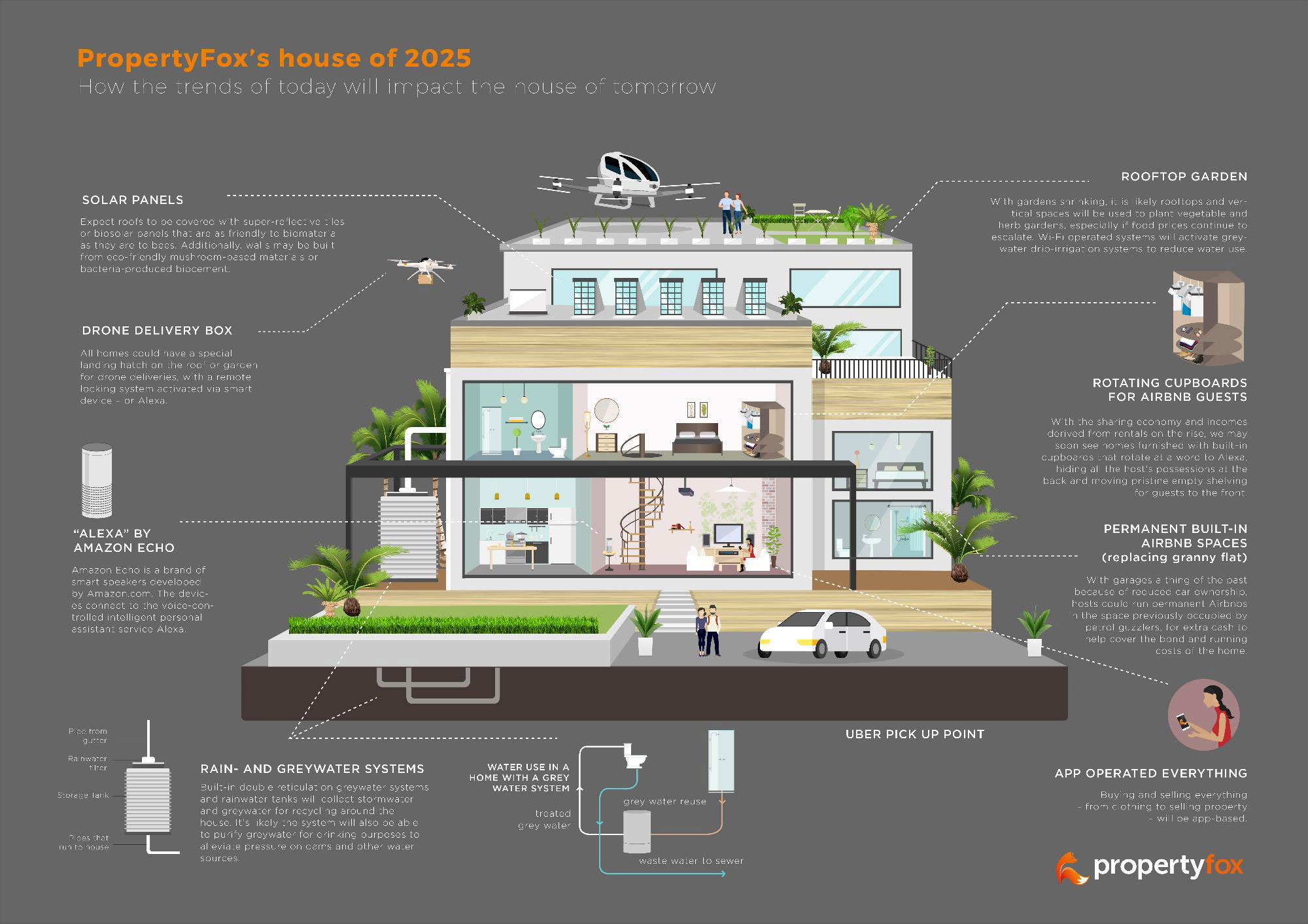
The construction industry is in a constant state of evolution, driven by technological advancements, changing demographics, and growing environmental concerns. As we approach 2025, several key trends are emerging, promising to reshape the way buildings are designed, constructed, and inhabited. These trends not only offer opportunities for innovation but also present challenges that must be addressed to ensure a sustainable and equitable future for the built environment.
Understanding the Driving Forces Behind Building Trends
Several factors are shaping the future of building trends:
- Technological Advancements: The rapid evolution of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, 3D printing, and Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing construction processes.
- Climate Change and Sustainability: The urgent need to mitigate climate change is driving a shift towards sustainable building practices, energy efficiency, and the use of renewable resources.
- Urbanization and Population Growth: Globally, populations are increasingly concentrated in urban areas, demanding innovative solutions for housing, infrastructure, and sustainable urban development.
- Changing Lifestyle Preferences: The rise of remote work, flexible living arrangements, and a growing focus on well-being are influencing the design and functionality of buildings.
Exploring the Key Building Trends for 2025
1. Smart Buildings and the Internet of Things (IoT):
* **Definition:** Smart buildings leverage interconnected devices and sensors to optimize building performance, enhance occupant comfort, and improve energy efficiency.
* **Examples:** Smart lighting systems that adjust to natural light levels, automated HVAC systems that optimize temperature and humidity, and security systems that integrate with mobile devices.
* **Benefits:** Reduced energy consumption, improved occupant comfort, enhanced security, increased operational efficiency, and valuable data insights for building management.
* **Challenges:** Data security concerns, interoperability issues between different systems, and the need for skilled personnel to manage and maintain complex IoT systems.2. Sustainable and Green Building Practices:
* **Definition:** Sustainable building practices prioritize resource conservation, energy efficiency, and environmental protection throughout the building lifecycle.
* **Examples:** Using recycled materials, incorporating renewable energy sources, implementing green roofs, and optimizing water usage.
* **Benefits:** Reduced environmental impact, lower operating costs, improved occupant health and well-being, and enhanced property value.
* **Challenges:** Higher initial construction costs, limited availability of sustainable materials, and the need for specialized expertise in sustainable building design.3. Modular and Prefabricated Construction:
* **Definition:** Modular construction involves assembling buildings from prefabricated components manufactured off-site, offering faster construction times and greater precision.
* **Examples:** Prefabricated walls, floors, and roofs, modular bathroom units, and pre-engineered structural components.
* **Benefits:** Reduced construction time, lower labor costs, improved quality control, and reduced waste on construction sites.
* **Challenges:** Limited design flexibility, potential transportation challenges, and the need for skilled labor to assemble modular components.4. 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing:
* **Definition:** 3D printing technology allows for the creation of complex building components and structures layer by layer, using materials like concrete, plastic, and metal.
* **Examples:** Printing architectural models, creating customized building elements, and constructing entire structures.
* **Benefits:** Greater design freedom, reduced waste, faster construction times, and the ability to create intricate and complex designs.
* **Challenges:** Limited scale of current 3D printing technology, material limitations, and the need for specialized expertise in 3D printing processes.5. Advanced Building Information Modeling (BIM):
* **Definition:** BIM is a digital representation of a building project, allowing for collaborative design, construction, and management throughout the building lifecycle.
* **Examples:** Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) tools for visualizing and interacting with BIM models, data analytics for optimizing building performance, and integrated project management platforms.
* **Benefits:** Improved communication and collaboration, reduced errors and rework, enhanced project planning and scheduling, and optimized building performance.
* **Challenges:** The need for skilled BIM professionals, data security concerns, and the need for standardized BIM protocols.6. Adaptive Reuse and Building Retrofitting:
* **Definition:** Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing buildings for new uses, while retrofitting involves upgrading existing buildings to meet modern standards and improve energy efficiency.
* **Examples:** Converting old factories into residential spaces, retrofitting office buildings with energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems.
* **Benefits:** Preservation of historic structures, reduced environmental impact, lower construction costs compared to new construction, and increased urban density.
* **Challenges:** Structural limitations of existing buildings, potential regulatory hurdles, and the need for careful planning and design.7. Human-Centric Design and Well-being:
* **Definition:** Human-centric design focuses on creating buildings that prioritize occupant well-being, comfort, and productivity.
* **Examples:** Creating spaces with natural light and ventilation, incorporating biophilic design elements, and designing for accessibility and inclusivity.
* **Benefits:** Improved occupant health and well-being, increased productivity, reduced stress levels, and a more positive and engaging work environment.
* **Challenges:** Balancing human-centric design principles with practical considerations like cost and functionality, and the need for ongoing research and data collection to understand the impact of design choices on occupant well-being.8. Robotics and Automation in Construction:
* **Definition:** Robotics and automation are increasingly being used in construction to improve efficiency, safety, and productivity.
* **Examples:** Robots for bricklaying, welding, and demolition, automated concrete pouring systems, and drones for site inspection and surveying.
* **Benefits:** Reduced labor costs, increased efficiency and productivity, improved safety on construction sites, and the ability to perform complex tasks with greater precision.
* **Challenges:** High initial investment costs, the need for skilled personnel to operate and maintain robotic systems, and potential job displacement concerns.Understanding the Importance of Building Trends
These trends are not simply stylistic choices; they are fundamental shifts in how we approach the design, construction, and operation of buildings. They offer numerous benefits, including:
- Environmental Sustainability: Reducing carbon footprint, conserving resources, and promoting renewable energy sources.
- Improved Occupant Well-being: Creating healthier, more comfortable, and productive spaces.
- Economic Growth: Creating new job opportunities, fostering innovation, and boosting economic competitiveness.
- Social Equity: Promoting accessibility, inclusivity, and equitable access to high-quality housing and infrastructure.
**Related Searches:
- Sustainable Building Materials: Explore the latest advancements in eco-friendly materials, such as bamboo, hempcrete, and recycled plastics, and their applications in construction.
- Building Automation Systems: Delve into the diverse range of building automation systems, including smart lighting, HVAC control, and security systems, and their role in creating intelligent and energy-efficient buildings.
- Green Building Certifications: Learn about various green building certifications, such as LEED and BREEAM, and their impact on promoting sustainable construction practices.
- Prefabricated Housing Trends: Investigate the growing popularity of prefabricated housing, its advantages, and the challenges it presents for the construction industry.
- Future of Construction Technology: Explore emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, robotics, and 3D printing and their potential to revolutionize the construction industry.
- Urban Planning and Design: Examine how building trends are influencing urban planning and design, focusing on sustainable urban development and creating livable cities.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Analyze how building codes and regulations are adapting to incorporate new technologies and sustainable practices.
- Construction Industry Workforce Development: Discuss the importance of training and education programs in preparing the construction workforce for the evolving demands of the industry.
FAQs about Building Trends 2025
1. What are the biggest challenges to implementing these building trends?
* **Cost:** Many of these trends, such as sustainable building materials and advanced technologies, can have higher initial costs compared to traditional methods.
* **Regulation:** Building codes and regulations can sometimes hinder the adoption of innovative technologies and practices.
* **Skilled Labor:** There is a growing need for skilled professionals who can design, build, and maintain buildings incorporating these new trends.
* **Public Awareness:** Raising awareness about the benefits of these trends and overcoming public skepticism is crucial for widespread adoption.2. How can architects and designers incorporate these trends into their projects?
* **Research and Stay Updated:** Continuously research and stay informed about the latest technologies and sustainable practices.
* **Collaborate with Specialists:** Work with engineers, sustainability consultants, and other experts to integrate these trends effectively.
* **Prioritize Human-Centric Design:** Focus on creating spaces that prioritize occupant well-being, comfort, and productivity.
* **Consider the Building Lifecycle:** Think about the long-term impacts of design choices on the building's environmental footprint, energy efficiency, and maintenance.3. What are the potential benefits of adopting these building trends?
* **Reduced Environmental Impact:** Lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced resource consumption, and improved air and water quality.
* **Enhanced Occupant Well-being:** Improved health, comfort, and productivity for building occupants.
* **Economic Growth and Innovation:** Creation of new job opportunities, fostering innovation in the construction industry, and driving economic growth.
* **Social Equity:** Promoting accessible and inclusive buildings, creating equitable access to high-quality housing and infrastructure.4. How can governments and policymakers support the adoption of these trends?
* **Incentives and Regulations:** Implement tax incentives, subsidies, and building codes that encourage the adoption of sustainable practices and innovative technologies.
* **Research and Development:** Invest in research and development to advance technologies and sustainable building materials.
* **Education and Training:** Support training programs to develop a skilled workforce capable of implementing these trends.
* **Public Awareness Campaigns:** Launch public awareness campaigns to educate citizens about the benefits of sustainable building practices.Tips for Embracing Building Trends 2025
- Start Small: Begin by implementing smaller-scale changes, such as using energy-efficient lighting or installing a green roof.
- Collaborate: Work with architects, engineers, and other professionals to integrate these trends effectively.
- Embrace Technology: Explore and adopt new technologies that can enhance building performance and efficiency.
- Prioritize Sustainability: Make sustainable building practices a core part of your design and construction processes.
- Stay Informed: Continuously research and stay updated on the latest trends and advancements in the industry.
Conclusion
Building trends 2025 represent a significant shift in how we design, build, and inhabit our spaces. These trends are driven by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and evolving lifestyle preferences. By embracing these trends, we can create a more sustainable, resilient, and equitable built environment for future generations. It is crucial for all stakeholders, including architects, builders, policymakers, and the public, to actively engage in this transformation, fostering innovation and ensuring a brighter future for the construction industry.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future: Building Trends for 2025 and Beyond. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!