Shaping the Future: Trends in Manufacturing 2025
Shaping the Future: Trends in Manufacturing 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future: Trends in Manufacturing 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shaping the Future: Trends in Manufacturing 2025

The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer demands. As we approach 2025, several key trends are shaping the future of this vital industry. Understanding these trends is crucial for manufacturers seeking to remain competitive and thrive in the coming years.
1. Digital Transformation: From Automation to Intelligent Systems
Digital transformation is no longer a buzzword but a reality for manufacturers. This trend encompasses the integration of digital technologies across all aspects of operations, from design and engineering to production and supply chain management.
- Automation: Robots and cobots are increasingly deployed to perform repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers for more complex and value-added activities. This leads to increased efficiency, reduced errors, and enhanced productivity.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered systems are used for predictive maintenance, quality control, and optimizing production processes. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and make intelligent decisions, further enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connected devices and sensors gather real-time data from the shop floor, enabling manufacturers to monitor production processes, track inventory, and identify potential issues proactively. This data-driven approach empowers informed decision-making and optimized operations.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based platforms provide manufacturers with scalable computing power and data storage solutions, enabling them to access and analyze data from anywhere, anytime. This fosters collaboration, reduces IT infrastructure costs, and facilitates faster innovation.
2. Sustainability: A Core Value for Modern Manufacturing
Sustainability is no longer a niche concern but a fundamental principle for manufacturers. Consumers are increasingly demanding products that are environmentally friendly and ethically produced.
- Circular Economy: Manufacturers are moving towards closed-loop systems, where waste is minimized and resources are reused or recycled. This approach reduces environmental impact and creates new business opportunities.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-saving technologies and practices is critical for reducing operational costs and minimizing carbon footprint. This includes using renewable energy sources, optimizing energy consumption, and adopting lean manufacturing principles.
- Sustainable Materials: Manufacturers are exploring and adopting sustainable materials, such as recycled plastics, bio-based polymers, and renewable resources. This shift towards eco-friendly materials aligns with consumer preferences and reduces environmental impact.
3. Personalization and Mass Customization:
Personalization is becoming the new standard in manufacturing. Consumers are demanding products tailored to their individual needs and preferences. This trend necessitates flexible production systems that can adapt to changing demands and produce customized products efficiently.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): 3D printing allows for the creation of highly customized products on demand, reducing lead times and minimizing waste. This technology is particularly relevant for prototyping, small-batch production, and personalized goods.
- Agile Manufacturing: Agile manufacturing principles focus on flexibility, responsiveness, and continuous improvement. Manufacturers are adopting lean methodologies and implementing agile processes to adapt to changing customer demands and market conditions.
- Digital Twins: Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets, allowing manufacturers to simulate and optimize production processes before implementation. This approach helps to reduce risk, improve efficiency, and facilitate rapid product development.
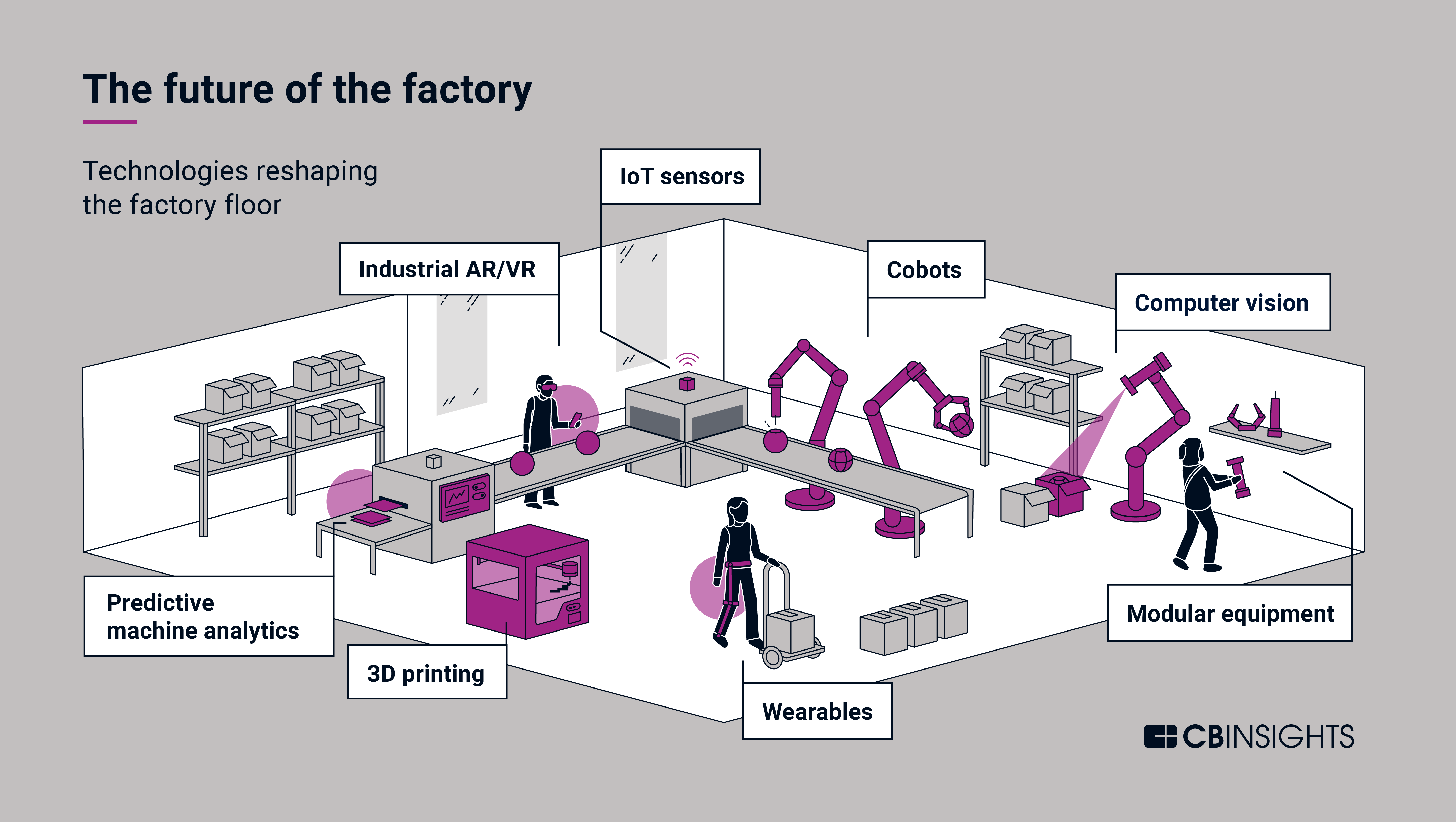
4. Advanced Robotics and Automation:
Advanced robotics and automation are revolutionizing manufacturing processes. Robots are becoming more intelligent, collaborative, and adaptable, enabling manufacturers to automate tasks that were previously impossible or too complex.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots are designed to work alongside humans, providing assistance and enhancing worker safety. These robots are particularly useful for tasks requiring precision, repetitive movements, or hazardous environments.
- Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs are automated vehicles that transport materials and products within manufacturing facilities. They improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance safety by eliminating manual handling tasks.
- Artificial Vision Systems: AI-powered vision systems are used for quality control, defect detection, and process monitoring. These systems can analyze images and videos in real-time, providing manufacturers with instant feedback and insights.
5. Supply Chain Resilience and Disruption Management:
Supply chain resilience is becoming paramount as global events and unforeseen circumstances can disrupt production and distribution networks. Manufacturers are actively seeking ways to mitigate risks and ensure a stable supply chain.
- Nearshoring and Reshoring: Companies are relocating production facilities closer to their markets or back to their home countries to reduce lead times, minimize transportation costs, and enhance control over their supply chains.
- Digital Supply Chain Management: Digital technologies are transforming supply chain operations, enabling real-time visibility, improved collaboration, and proactive risk management. This includes using blockchain technology for secure and transparent transactions.
- Supply Chain Diversification: Manufacturers are diversifying their supplier networks to mitigate risks associated with single-source dependence. This approach ensures access to critical materials and components even in the face of disruptions.
6. The Rise of the Skilled Workforce:
The skilled workforce is essential for navigating the technological advancements and complex challenges in modern manufacturing. Companies are investing in training programs to upskill their employees and prepare them for the future of work.
- Upskilling and Reskilling Programs: Manufacturers are offering training programs to equip their employees with the skills needed to operate advanced technologies, analyze data, and solve complex problems.
- STEM Education: Promoting STEM education (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) is crucial for developing a future workforce equipped with the skills necessary for the manufacturing industry.
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: Manufacturers are focusing on creating a positive work environment, offering competitive salaries and benefits, and promoting career advancement opportunities to attract and retain skilled workers.
7. Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance:
Data analytics and predictive maintenance are becoming increasingly important for optimizing operations, reducing downtime, and improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
- Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered systems analyze sensor data from machines to predict potential failures and schedule maintenance proactively. This approach reduces unplanned downtime, minimizes repair costs, and extends equipment lifespan.
- Data-Driven Optimization: Manufacturers are using data analytics to identify bottlenecks in production processes, optimize material flow, and improve resource allocation. This data-driven approach leads to increased efficiency, reduced waste, and enhanced productivity.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Real-time data monitoring allows manufacturers to track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify deviations from expected behavior, and intervene quickly to prevent problems. This approach enables proactive problem-solving and ensures optimal performance.
8. Cybersecurity: Protecting Manufacturing Systems:
Cybersecurity is a critical concern for manufacturers as they increasingly rely on interconnected systems and digital technologies. Protecting sensitive data, ensuring operational continuity, and mitigating cyber threats are essential.
- Network Security: Implementing robust network security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure access controls, is crucial for protecting manufacturing systems from unauthorized access.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit is essential for safeguarding confidential information from unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
- Employee Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices, including password hygiene, phishing awareness, and data security protocols, is crucial for mitigating human error and reducing the risk of cyberattacks.
Related Searches
1. Future of Manufacturing:
The future of manufacturing is characterized by a convergence of digital technologies, sustainability initiatives, and evolving consumer demands. Manufacturers are embracing automation, AI, and other digital tools to optimize operations, enhance efficiency, and meet the growing need for personalization. Sustainability is becoming a core value, driving innovation in circular economy practices, energy efficiency, and sustainable materials.
2. Industry 4.0 Manufacturing:
Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes. This includes automation, AI, IoT, cloud computing, and advanced robotics. Industry 4.0 is transforming the way goods are designed, produced, and delivered, enabling greater efficiency, flexibility, and responsiveness.
3. Smart Manufacturing:
Smart manufacturing refers to the use of digital technologies to create intelligent and interconnected factories. This involves integrating sensors, data analytics, and AI to optimize production processes, enhance quality control, and improve decision-making. Smart factories are becoming more flexible, responsive, and adaptable to changing market conditions.
4. Advanced Manufacturing Technologies:
Advanced manufacturing technologies encompass a wide range of innovations, including robotics, automation, additive manufacturing (3D printing), advanced materials, and digital twins. These technologies are enabling manufacturers to create new products, improve efficiency, and enhance sustainability.
5. Manufacturing Trends 2023:
The manufacturing trends in 2023 are closely aligned with the broader trends shaping the industry in 2025. Key themes include the continued adoption of digital technologies, increasing focus on sustainability, and the growing importance of workforce skills. Manufacturers are adapting to evolving consumer demands, supply chain disruptions, and the need to operate more efficiently and sustainably.
6. Manufacturing Industry Outlook:
The manufacturing industry outlook for the coming years is positive, driven by technological advancements, growing global demand, and increasing investment in research and development. However, manufacturers face challenges related to talent acquisition, supply chain disruptions, and the need to adapt to evolving market conditions.
7. Manufacturing Innovation:
Manufacturing innovation encompasses the development and application of new technologies, processes, and business models to create value and enhance competitiveness. Innovation is crucial for manufacturers to stay ahead of the curve, address evolving customer needs, and remain competitive in a rapidly changing global landscape.
8. Impact of Technology on Manufacturing:
Technology is having a profound impact on manufacturing, enabling automation, data-driven decision-making, and enhanced efficiency. Digital technologies are transforming the way goods are designed, produced, and delivered, creating new opportunities and challenges for manufacturers.
FAQs
1. What are the benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing?
Digital transformation offers numerous benefits for manufacturers, including:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation and AI-powered systems streamline production processes, reducing errors and increasing throughput.
- Enhanced Productivity: Optimizing operations and reducing downtime leads to higher productivity and increased output.
- Improved Quality Control: Real-time data monitoring and AI-powered vision systems enable manufacturers to identify and address quality issues proactively.
- Reduced Costs: Automation, efficiency improvements, and data-driven decision-making lead to lower operational costs and increased profitability.
- Faster Innovation: Digital tools facilitate rapid prototyping, design iterations, and product development, enabling manufacturers to bring new products to market faster.
2. How can manufacturers achieve sustainability in their operations?
Manufacturers can achieve sustainability through a combination of strategies, including:
- Implementing Circular Economy Principles: Reducing waste, reusing materials, and recycling resources to minimize environmental impact.
- Adopting Energy Efficiency Measures: Using renewable energy sources, optimizing energy consumption, and implementing energy-saving technologies.
- Utilizing Sustainable Materials: Sourcing materials from renewable resources, recycled materials, or eco-friendly alternatives.
- Reducing Carbon Footprint: Minimizing emissions through energy efficiency measures, sustainable transportation, and responsible waste management.
- Promoting Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring that materials and components are sourced from suppliers that adhere to ethical and environmental standards.
3. What are the challenges of adopting advanced robotics and automation?
While advanced robotics and automation offer significant benefits, manufacturers face challenges in implementing these technologies, including:
- High Initial Investment Costs: Robotics and automation systems can be expensive to purchase and install.
- Skill Gap: A skilled workforce is required to operate, maintain, and program advanced robotic systems.
- Job Displacement: Automation can lead to job displacement, requiring manufacturers to address workforce retraining and reskilling.
- Safety Concerns: Ensuring the safety of workers working alongside robots is critical, requiring careful planning and implementation.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating robotic systems into existing production lines can be complex and require careful planning and testing.
4. How can manufacturers build a resilient supply chain?
Manufacturers can build a resilient supply chain by:
- Nearshoring or Reshoring Production: Relocating production facilities closer to markets or back to home countries to reduce lead times and minimize disruptions.
- Diversifying Supplier Networks: Working with multiple suppliers to reduce dependence on single sources and mitigate risks.
- Implementing Digital Supply Chain Management: Using technologies like blockchain and real-time tracking to improve visibility, collaboration, and risk management.
- Building Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with suppliers and logistics providers to enhance communication, coordination, and resilience.
- Developing Contingency Plans: Creating backup plans and alternative sourcing strategies to mitigate disruptions caused by unexpected events.
Tips
- Embrace Continuous Improvement: Adopt a culture of continuous improvement, seeking ways to optimize processes, reduce waste, and enhance efficiency.
- Invest in Workforce Development: Invest in training programs to upskill employees and prepare them for the future of work, equipping them with the skills needed to operate advanced technologies and solve complex problems.
- Foster Innovation: Encourage creativity and experimentation, exploring new technologies and processes to improve products, enhance efficiency, and create new business opportunities.
- Collaborate with Partners: Collaborate with suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders to share knowledge, develop solutions, and build a stronger ecosystem.
- Stay Informed about Trends: Continuously monitor industry trends, technological advancements, and evolving consumer demands to stay ahead of the curve and adapt to changing market conditions.
Conclusion
Trends in manufacturing 2025 are shaping the future of this vital industry, driving innovation, efficiency, and sustainability. By embracing digital transformation, prioritizing sustainability, and investing in a skilled workforce, manufacturers can navigate these trends and emerge as leaders in a rapidly evolving global landscape. The future of manufacturing is bright, characterized by intelligent systems, personalized products, and a commitment to responsible practices.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future: Trends in Manufacturing 2025. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!