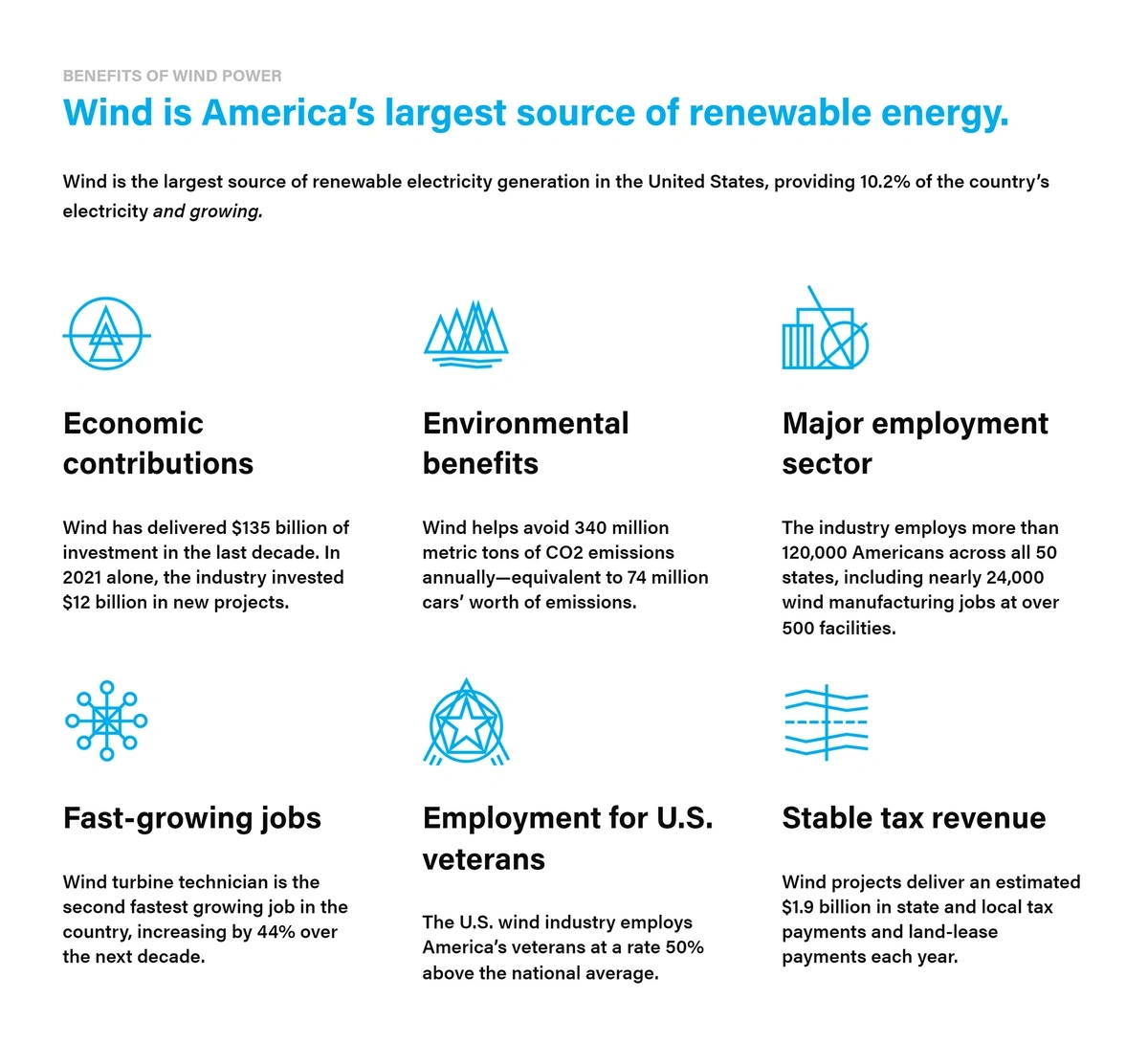
Sustainability Trends 2025: Shaping a Sustainable Future
Sustainability Trends 2025: Shaping a Sustainable Future
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Sustainability Trends 2025: Shaping a Sustainable Future. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Sustainability Trends 2025: Shaping a Sustainable Future
The year 2025 is fast approaching, and with it, a wave of transformative trends in the realm of sustainability. These trends are not merely fleeting fads; they represent a fundamental shift in how we live, work, and consume. Driven by escalating environmental concerns, technological advancements, and a growing awareness of the interconnectedness of our planet, these trends are poised to reshape our societies and economies.
Understanding Sustainability Trends 2025
Sustainability trends 2025 encompass a broad spectrum of changes across various sectors. These trends are not isolated phenomena but rather interconnected threads woven into a complex tapestry of progress. They are driven by a confluence of factors, including:
- Climate Change: The growing urgency of climate change compels individuals, businesses, and governments to adopt sustainable practices.
- Resource Depletion: As finite resources dwindle, innovative solutions are being sought to optimize resource utilization and minimize waste.
- Technological Advancements: Technological breakthroughs are facilitating the development of sustainable solutions in areas such as renewable energy, circular economy, and smart cities.
- Consumer Demand: Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable products and services, influencing businesses to prioritize environmental and social responsibility.
- Government Regulations: Governments are implementing stricter regulations to promote sustainability, incentivize environmentally friendly practices, and penalize unsustainable behavior.
Exploring Key Sustainability Trends 2025
1. Circular Economy:
The linear "take, make, dispose" model of production and consumption is unsustainable. The circular economy promotes a closed-loop system where resources are constantly reused and recycled, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency.
-
Key Features:
- Product Durability and Reusability: Designing products for longevity and ease of repair to extend their lifespan.
- Closed-Loop Manufacturing: Incorporating recycling and repurposing processes into production cycles.
- Waste Reduction and Recycling: Implementing efficient waste management systems and promoting responsible recycling practices.
- Sharing and Leasing Models: Encouraging sharing platforms and leasing options to reduce individual ownership and consumption.
-
Benefits:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Minimizes resource extraction, pollution, and landfill waste.
- Economic Growth: Creates new business opportunities and promotes innovation in resource management.
- Job Creation: Fosters employment in circular economy-related industries.
2. Renewable Energy:
The transition to renewable energy sources is a cornerstone of sustainable development. Solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass energy are gaining traction as viable alternatives to fossil fuels.
-
Key Features:
- Decentralized Energy Systems: Shifting from centralized power grids to local, distributed generation systems.
- Energy Storage Solutions: Developing advanced technologies for storing renewable energy for later use.
- Smart Grids: Implementing intelligent infrastructure to manage energy flow and optimize grid efficiency.
-
Benefits:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Minimizes carbon footprint and combats climate change.
- Energy Security: Reduces dependence on fossil fuels and enhances national energy security.
- Economic Growth: Creates new jobs and stimulates investment in renewable energy technologies.
3. Sustainable Agriculture:
Agriculture is a major contributor to environmental degradation, but sustainable practices can mitigate its impact. Organic farming, regenerative agriculture, and precision agriculture are key trends in this area.
-
Key Features:
- Organic Farming: Avoiding synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms.
- Regenerative Agriculture: Focusing on soil health, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration.
- Precision Agriculture: Using technology to optimize resource use and minimize waste.
-
Benefits:
- Improved Soil Health: Enhances soil fertility, water retention, and biodiversity.
- Reduced Pollution: Minimizes pesticide and fertilizer runoff into waterways.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Promotes carbon sequestration and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
4. Sustainable Transportation:
The transportation sector is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions. Electric vehicles, autonomous vehicles, and shared mobility are emerging as sustainable alternatives.
-
Key Features:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Transitioning from gasoline-powered vehicles to electric vehicles powered by renewable energy.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Developing self-driving cars and trucks to improve efficiency and safety.
- Shared Mobility: Promoting ride-sharing, car-pooling, and public transportation to reduce individual vehicle ownership.
-
Benefits:
- Reduced Emissions: Minimizes greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
- Improved Traffic Flow: Optimizes road use and reduces congestion.
- Enhanced Safety: Autonomous vehicles have the potential to reduce accidents.
5. Sustainable Buildings:
Buildings account for a substantial portion of global energy consumption and emissions. Sustainable building practices aim to minimize environmental impact while enhancing occupant health and well-being.
-
Key Features:
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-saving technologies and building materials.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Incorporating solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy sources.
- Water Conservation: Installing water-efficient fixtures and implementing rainwater harvesting systems.
- Green Building Materials: Using sustainable and eco-friendly building materials.
-
Benefits:
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Minimizes reliance on fossil fuels and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Lower Operating Costs: Reduces energy and water bills for building owners and occupants.
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: Promotes healthier indoor environments.
6. Sustainable Packaging:
Packaging plays a crucial role in product distribution and protection but often contributes to waste. Sustainable packaging options are gaining popularity, focusing on reusability, recyclability, and biodegradability.
-
Key Features:
- Reusable Packaging: Designing packaging that can be used multiple times before disposal.
- Recyclable Packaging: Utilizing materials that can be easily recycled into new products.
- Biodegradable Packaging: Employing materials that decompose naturally over time.
- Minimalist Packaging: Reducing the amount of packaging material used for each product.
-
Benefits:
- Reduced Waste: Minimizes landfill waste and promotes resource conservation.
- Environmental Protection: Reduces pollution and deforestation associated with packaging production.
- Consumer Trust: Builds consumer confidence in brands committed to sustainability.
7. Sustainable Fashion:
The fashion industry is notorious for its environmental and social impacts. Sustainable fashion practices address these concerns by prioritizing ethical sourcing, eco-friendly materials, and responsible manufacturing processes.
-
Key Features:
- Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring that materials are sourced from sustainable and responsible suppliers.
- Organic and Recycled Materials: Utilizing organic cotton, recycled polyester, and other eco-friendly fabrics.
- Fair Labor Practices: Supporting fair wages, safe working conditions, and ethical treatment of workers.
- Circular Fashion: Promoting clothing rental, repair, and resale to extend the lifespan of garments.
-
Benefits:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Minimizes pollution, resource depletion, and waste associated with fashion production.
- Improved Social Responsibility: Ensures fair treatment of workers and promotes ethical labor practices.
- Increased Transparency: Provides consumers with information about the origins and production processes of their clothing.
8. Sustainable Tourism:
Tourism can have significant environmental and social impacts. Sustainable tourism aims to minimize these impacts while promoting local communities and preserving cultural heritage.
-
Key Features:
- Ecotourism: Focusing on nature-based experiences and responsible environmental practices.
- Community-Based Tourism: Supporting local communities and their economic development.
- Sustainable Accommodation: Utilizing eco-friendly hotels and lodging options.
- Responsible Travel: Promoting responsible travel behaviors, such as reducing waste and minimizing carbon footprint.
-
Benefits:
- Environmental Conservation: Protects natural ecosystems and promotes biodiversity.
- Community Empowerment: Supports local economies and empowers communities.
- Cultural Preservation: Preserves cultural heritage and traditions.
Related Searches
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): The 17 SDGs adopted by the United Nations provide a comprehensive framework for achieving sustainable development.
- Green Technology: This refers to technologies and innovations that promote environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and waste management solutions.
- ESG Investing: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investing is a growing trend that considers sustainability factors in investment decisions.
- Climate Action: Initiatives and efforts aimed at mitigating climate change and adapting to its impacts.
- Circular Economy Business Models: Exploring business models that embrace the principles of the circular economy.
- Sustainable Supply Chains: Building supply chains that prioritize environmental and social responsibility.
- Sustainable Consumption: Promoting responsible consumption patterns and reducing waste.
FAQs by Sustainability Trends 2025
1. What are the benefits of adopting sustainability trends 2025?
Adopting sustainability trends 2025 offers numerous benefits, including:
- Environmental Protection: Reducing pollution, resource depletion, and climate change.
- Economic Growth: Creating new business opportunities and stimulating innovation.
- Social Equity: Promoting fair labor practices, community development, and social justice.
- Improved Quality of Life: Enhancing health, well-being, and overall quality of life.
2. How can individuals contribute to sustainability trends 2025?
Individuals can contribute to sustainability trends 2025 by:
- Adopting Sustainable Practices: Reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and choosing sustainable products and services.
- Supporting Sustainable Businesses: Patronizing companies that prioritize environmental and social responsibility.
- Advocating for Change: Engaging in public discourse and advocating for policies that promote sustainability.
- Spreading Awareness: Educating others about the importance of sustainability and inspiring them to take action.
3. How are businesses responding to sustainability trends 2025?
Businesses are increasingly responding to sustainability trends 2025 by:
- Integrating Sustainability into Business Strategies: Incorporating environmental and social considerations into core business operations.
- Developing Sustainable Products and Services: Offering products and services that meet the needs of environmentally conscious consumers.
- Investing in Green Technology: Investing in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and other sustainable technologies.
- Reporting on Sustainability Performance: Providing transparent information about their environmental and social impact.
4. What are the challenges to implementing sustainability trends 2025?
Implementing sustainability trends 2025 faces challenges, including:
- Cost of Sustainable Solutions: Sustainable solutions can be more expensive upfront compared to conventional alternatives.
- Lack of Awareness and Education: Many individuals and businesses lack awareness and understanding of sustainability principles.
- Policy and Regulatory Barriers: Existing policies and regulations may hinder the adoption of sustainable practices.
- Technological Limitations: Some sustainable technologies are still under development and require further advancements.
5. What is the role of government in promoting sustainability trends 2025?
Governments play a crucial role in promoting sustainability trends 2025 by:
- Setting Policy Targets: Establishing ambitious targets for reducing emissions, promoting renewable energy, and conserving resources.
- Providing Incentives: Offering financial incentives and tax breaks to encourage sustainable practices.
- Implementing Regulations: Enacting regulations to promote sustainable behavior and penalize unsustainable activities.
- Investing in Research and Development: Funding research and development of sustainable technologies and solutions.
Tips by Sustainability Trends 2025
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Embrace the three R’s of sustainability to minimize waste and conserve resources.
- Choose Sustainable Products: Opt for products made from recycled or renewable materials and packaged sustainably.
- Support Local Businesses: Patronize businesses that prioritize sustainability and community development.
- Reduce Your Carbon Footprint: Minimize your carbon footprint by using public transportation, walking, cycling, and reducing energy consumption.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Learn about sustainability issues and share your knowledge with others to promote awareness.
Conclusion by Sustainability Trends 2025
Sustainability trends 2025 represent a pivotal moment in human history. They present an opportunity to address the urgent challenges of climate change, resource depletion, and social inequality. By embracing these trends, we can create a more sustainable, equitable, and resilient future for generations to come.
This transformative journey requires collective action from individuals, businesses, and governments. It necessitates a paradigm shift in how we think, consume, and interact with the environment. By embracing the principles of sustainability, we can pave the way for a future where economic prosperity and environmental well-being go hand in hand.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Sustainability Trends 2025: Shaping a Sustainable Future. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!