The Future of Healthcare: Trends Shaping the Medical Landscape by 2025
The Future of Healthcare: Trends Shaping the Medical Landscape by 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Future of Healthcare: Trends Shaping the Medical Landscape by 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Future of Healthcare: Trends Shaping the Medical Landscape by 2025

The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing demographics, and a growing emphasis on preventative care and personalized medicine. As we approach 2025, several key trends are poised to reshape the medical landscape, significantly impacting how healthcare is delivered, accessed, and experienced.
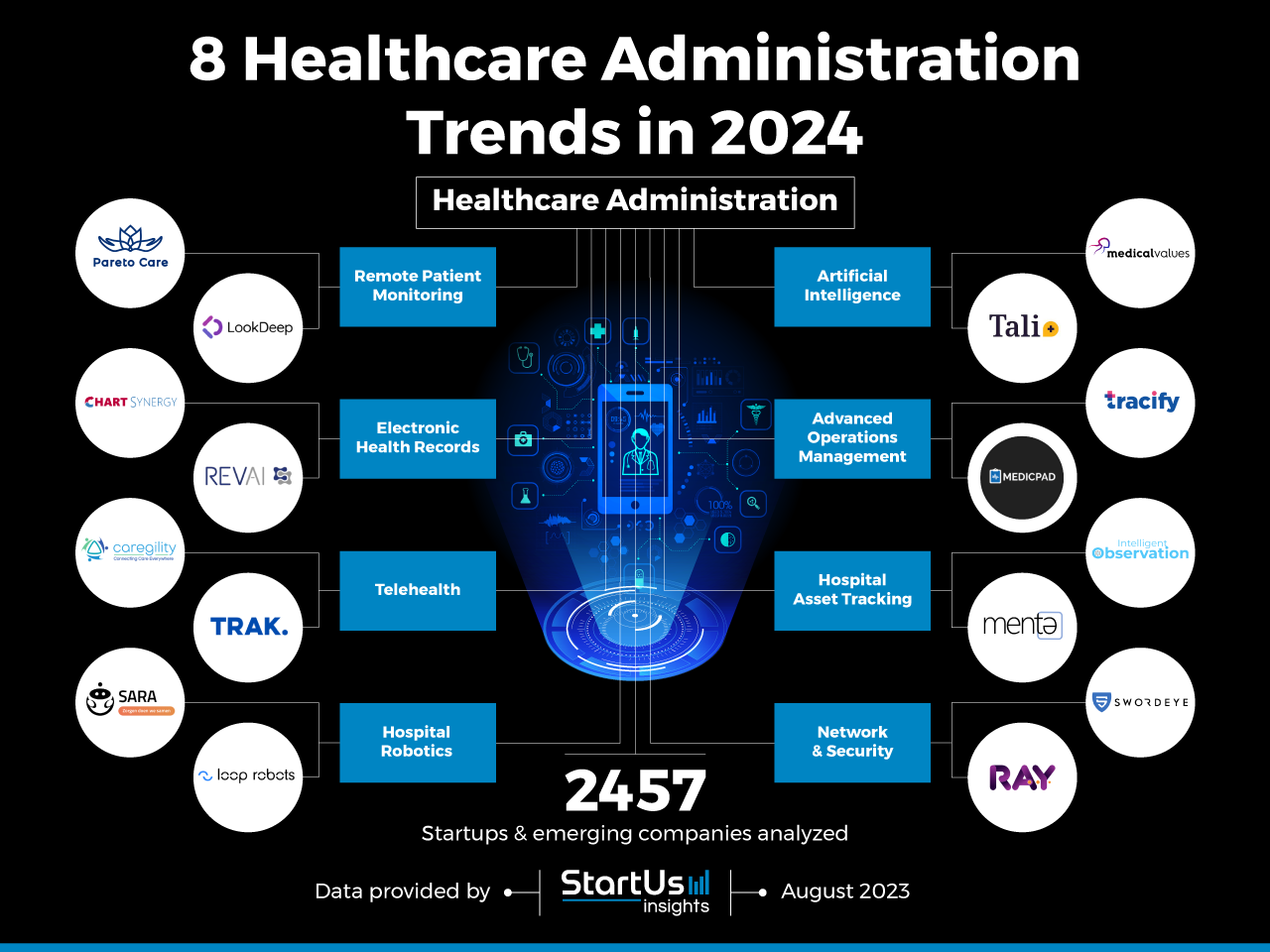
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are rapidly transforming healthcare, from diagnosis and treatment planning to drug discovery and personalized medicine. These technologies enable:
- Enhanced Diagnosis: AI-powered algorithms can analyze medical images, patient data, and genetic information to identify diseases earlier and more accurately than traditional methods.
- Predictive Analytics: By analyzing patient data, AI can identify individuals at risk for specific conditions, enabling proactive interventions and preventative care.
- Drug Discovery and Development: AI can accelerate drug discovery by identifying potential drug candidates and optimizing clinical trials.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: AI can tailor treatment plans based on a patient’s individual genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history.
Benefits of AI in Healthcare:
- Improved Accuracy and Efficiency: AI can assist healthcare professionals in making more accurate diagnoses and treatment decisions, leading to better outcomes.
- Reduced Costs: AI can automate routine tasks, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on more complex cases and reducing overall costs.
- Enhanced Patient Care: AI can provide personalized care and support, improving patient satisfaction and adherence to treatment plans.
Examples of AI in Healthcare:
- IBM Watson: A platform that uses AI to assist oncologists in developing personalized treatment plans for cancer patients.
- Google DeepMind: Developed an AI system that can detect diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of blindness, from retinal images.
- PathAI: Utilizes AI to analyze pathology slides, improving the accuracy and speed of cancer diagnosis.
2. Telemedicine and Virtual Care
Telemedicine, the use of technology to deliver healthcare remotely, is experiencing explosive growth. The pandemic further accelerated this trend, highlighting its potential for providing convenient, accessible, and affordable healthcare.
Key Aspects of Telemedicine:
- Remote Consultations: Patients can consult with healthcare providers virtually, eliminating the need for travel and reducing wait times.
- Remote Monitoring: Wearable devices and remote monitoring systems allow patients to track their health metrics and share data with their providers.
- Virtual Therapy: Telemedicine enables patients to access mental health services, such as therapy and counseling, from the comfort of their homes.
Benefits of Telemedicine:
- Increased Access to Care: Telemedicine expands access to healthcare services, particularly for those living in rural or underserved areas.
- Reduced Costs: Telemedicine can reduce healthcare costs by minimizing travel expenses and hospital admissions.
- Convenience and Flexibility: Patients can access care at their convenience, reducing the need for time off from work or school.
Examples of Telemedicine Services:
- Teladoc: A leading provider of virtual care services, offering remote consultations, medication management, and mental health services.
- MDLive: Provides virtual consultations with board-certified physicians, covering a wide range of medical conditions.
- American Well: Offers telehealth solutions for hospitals, health systems, and employers, enabling virtual consultations and remote patient monitoring.
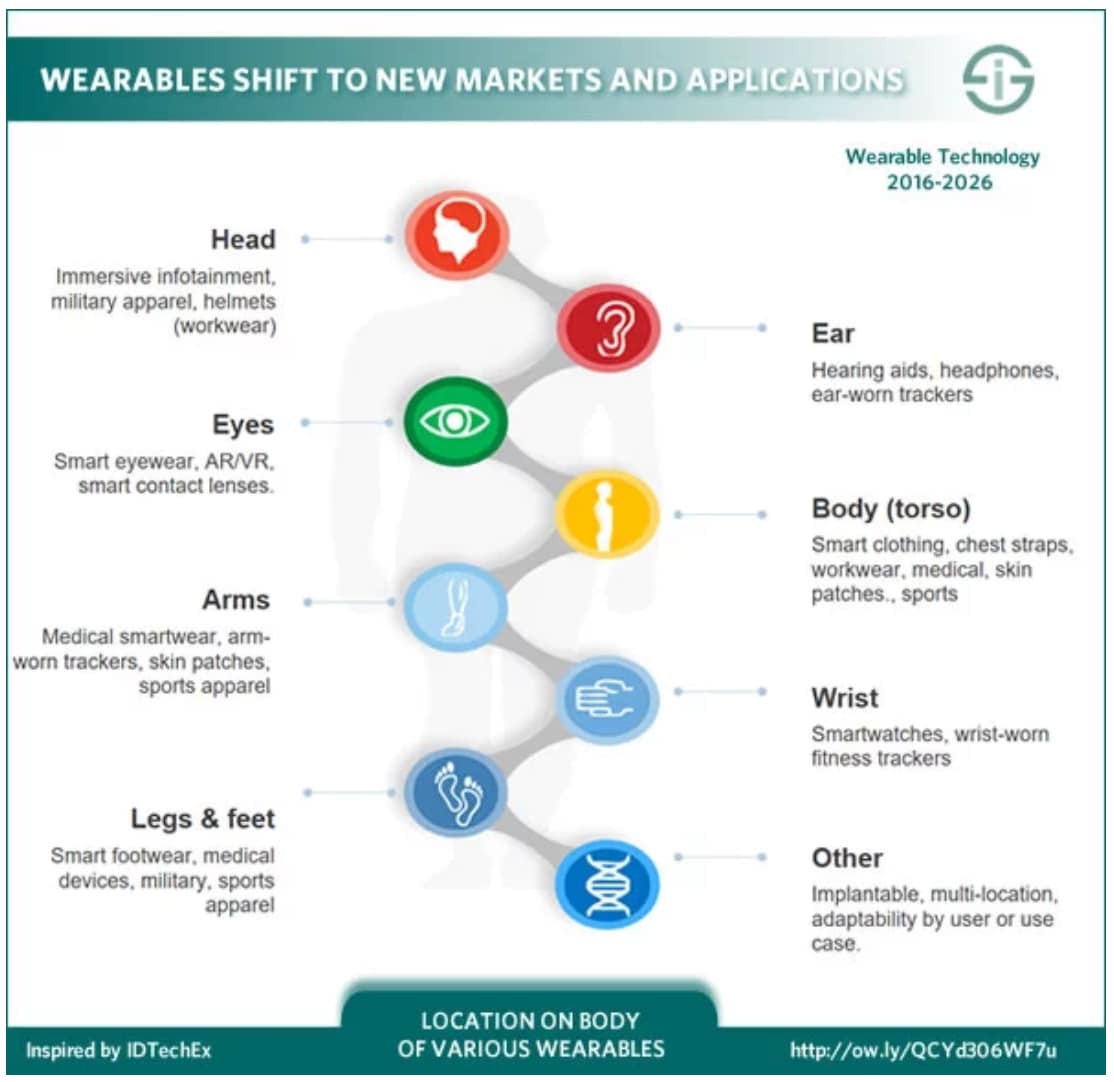
3. Wearable Technology and Consumer Health Data
Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, are becoming increasingly popular, providing individuals with real-time insights into their health. This trend is fueling the growth of consumer health data, which can be used to improve healthcare outcomes and personalize care.
Key Features of Wearable Technology:
- Activity Tracking: Monitors steps, distance, calories burned, and sleep patterns.
- Heart Rate Monitoring: Tracks heart rate variability and provides insights into cardiovascular health.
- Blood Glucose Monitoring: Enables individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels.
- GPS Tracking: Tracks location and can be used for emergency response and fall detection.
Benefits of Wearable Technology and Consumer Health Data:
- Empowerment and Self-Monitoring: Individuals can take a more active role in managing their health and wellness.
- Early Detection of Health Issues: Wearable devices can identify potential health problems early, allowing for timely intervention.
- Personalized Health Insights: Data collected from wearable devices can be used to personalize healthcare recommendations and treatment plans.
- Research and Innovation: Consumer health data provides valuable insights for researchers and healthcare professionals, driving innovation in healthcare.
Examples of Wearable Technology Companies:
- Fitbit: Offers a range of fitness trackers that monitor activity, heart rate, sleep, and other health metrics.
- Apple Watch: A smartwatch that provides health and fitness tracking features, including ECG monitoring and fall detection.
- Garmin: Manufactures GPS-enabled fitness trackers and smartwatches with advanced health monitoring capabilities.
4. Big Data and Analytics
The increasing availability of health data, combined with advancements in data analytics, is transforming healthcare research, decision-making, and care delivery.
Key Applications of Big Data in Healthcare:
- Population Health Management: Analyzing large datasets to identify health trends, predict outbreaks, and target interventions.
- Precision Medicine: Tailoring treatment plans based on individual patient data, including genetic information, lifestyle factors, and environmental exposures.
- Clinical Trial Optimization: Using data to improve the design, recruitment, and analysis of clinical trials, leading to faster and more efficient drug development.
- Fraud Detection: Identifying and preventing fraudulent activities in the healthcare system.
Benefits of Big Data and Analytics in Healthcare:
- Improved Healthcare Outcomes: By identifying patterns and trends in data, healthcare providers can make more informed decisions and deliver more effective care.
- Increased Efficiency: Data analytics can streamline processes and improve operational efficiency in healthcare organizations.
- Cost Reduction: Identifying areas of waste and inefficiency can help reduce healthcare costs.
- Enhanced Research: Big data provides valuable insights for researchers, accelerating the pace of medical discovery.
5. Genomics and Personalized Medicine
Genomics, the study of an organism’s complete set of genes, is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling personalized medicine. This approach tailors treatment plans based on an individual’s unique genetic makeup, leading to more effective and targeted therapies.
Key Aspects of Genomics in Healthcare:
- Genetic Testing: Identifies genetic variations that may increase an individual’s risk for certain diseases.
- Pharmacogenomics: Determines how an individual’s genes might affect their response to different medications.
- Cancer Genomics: Identifies specific genetic mutations in cancer cells to guide personalized treatment strategies.
Benefits of Personalized Medicine:
- Increased Treatment Effectiveness: By targeting therapies to individual genetic profiles, personalized medicine can improve treatment outcomes and reduce side effects.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Personalized medicine can potentially reduce healthcare costs by preventing unnecessary treatments and minimizing adverse events.
- Empowered Patients: Genomics provides individuals with a deeper understanding of their health risks and empowers them to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Examples of Personalized Medicine Applications:
- Genetic Testing for Cancer Risk: Companies like 23andMe and AncestryDNA offer genetic tests that can identify variations associated with an increased risk for certain cancers.
- Pharmacogenomics for Drug Response: Doctors can use pharmacogenomic testing to determine which medications are most likely to be effective for a particular patient based on their genetic makeup.
- Cancer Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy treatments are tailored to individual patients based on their tumor’s genetic profile.
6. Blockchain and Cybersecurity
Blockchain technology, known for its secure and transparent nature, is emerging as a potential solution for improving data security and interoperability in healthcare.
Key Applications of Blockchain in Healthcare:
- Secure Data Storage and Sharing: Blockchain can provide a secure and tamper-proof platform for storing and sharing patient health records.
- Improved Interoperability: Blockchain can facilitate seamless data exchange between different healthcare providers, improving patient care coordination.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the movement of pharmaceuticals and medical devices, ensuring their authenticity and safety.
Benefits of Blockchain in Healthcare:
- Enhanced Data Security: Blockchain’s decentralized and encrypted nature enhances data security and protects patient privacy.
- Improved Data Integrity: Blockchain ensures the immutability of data, preventing alteration or tampering.
- Increased Transparency: Blockchain provides a transparent and auditable record of data transactions, promoting accountability and trust.
7. Digital Health and Mobile Apps
Mobile health apps are becoming increasingly prevalent, providing patients with access to a wide range of healthcare services and information at their fingertips.
Key Features of Digital Health Apps:
- Health Tracking: Monitor fitness, sleep, nutrition, and other health metrics.
- Medication Reminders: Help patients stay on track with their medication schedules.
- Symptom Checkers: Provide initial assessments of health concerns.
- Telemedicine Consultations: Facilitate virtual consultations with healthcare providers.
- Mental Health Support: Offer tools for managing stress, anxiety, and depression.
Benefits of Digital Health Apps:
- Increased Patient Engagement: Mobile apps empower patients to take an active role in their health management.
- Improved Patient Education: Apps provide access to reliable health information and educational resources.
- Convenient Access to Care: Digital health apps offer convenient and accessible healthcare services.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Mobile apps can reduce healthcare costs by facilitating self-management and reducing unnecessary visits to healthcare providers.
8. Value-Based Care and Population Health Management
Value-based care (VBC) focuses on delivering high-quality care while controlling costs. It emphasizes preventative care, population health management, and improving patient outcomes.
Key Principles of Value-Based Care:
- Quality over Quantity: Healthcare providers are rewarded for delivering high-quality care rather than simply providing more services.
- Patient Engagement: Encourages patients to take an active role in their health management.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Utilizes data to identify areas for improvement and measure the effectiveness of care interventions.
- Accountability and Transparency: Healthcare providers are held accountable for the quality and cost of care they deliver.
Benefits of Value-Based Care:
- Improved Healthcare Outcomes: By focusing on quality and patient outcomes, VBC aims to improve the overall health of the population.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: VBC models incentivize healthcare providers to provide cost-effective care, leading to lower healthcare expenditures.
- Enhanced Patient Experience: VBC emphasizes patient engagement and satisfaction, improving the overall healthcare experience.
Examples of Value-Based Care Initiatives:
- Medicare Advantage: A private health insurance program that offers value-based care options to Medicare beneficiaries.
- Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs): Networks of healthcare providers that share responsibility for the quality and cost of care delivered to a defined patient population.
- Bundled Payments: A payment model where healthcare providers receive a single payment for a specific episode of care, incentivizing them to deliver efficient and coordinated care.
Related Searches
1. Healthcare Technology Trends 2025
This search explores the specific technological advancements shaping the healthcare industry in the coming years. It delves deeper into the impact of AI, big data, blockchain, and other technologies on healthcare delivery, research, and patient care.
2. Future of Healthcare 2025
This search focuses on the broader vision of healthcare in 2025, considering not only technological advancements but also societal changes and evolving patient expectations. It examines how these factors will influence the healthcare landscape and the role of healthcare professionals in the future.
3. Healthcare Industry Trends 2025
This search provides a comprehensive overview of the key trends impacting the healthcare industry as a whole, including economic factors, regulatory changes, and market dynamics. It explores how these trends will shape the industry’s future and the opportunities and challenges they present.
4. Healthcare Innovation 2025
This search focuses on the innovations driving progress in healthcare, including new medical devices, pharmaceutical breakthroughs, and advancements in diagnostics and treatments. It explores the impact of these innovations on patient care and the future of healthcare.
5. Digital Health Trends 2025
This search delves into the growing role of digital health in healthcare, examining the impact of mobile apps, wearable devices, telehealth, and other digital technologies on patient engagement, access to care, and healthcare outcomes.
6. Healthcare Workforce Trends 2025
This search analyzes the changing dynamics of the healthcare workforce, including workforce shortages, evolving job roles, and the impact of technology on healthcare professionals. It explores the challenges and opportunities for healthcare professionals in the future.
7. Healthcare Policy Trends 2025
This search examines the evolving healthcare policy landscape, including changes in regulations, reimbursement models, and healthcare financing. It explores the impact of these policy shifts on healthcare delivery and access to care.
8. Healthcare Consumerism 2025
This search explores the growing trend of healthcare consumerism, where patients are becoming more informed and demanding in their healthcare choices. It examines how this trend is influencing the healthcare industry and the need for patient-centered care.
FAQs
1. How will AI and ML impact healthcare by 2025?
AI and ML are expected to play a significant role in transforming healthcare by 2025, enabling more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and efficient drug discovery. These technologies will assist healthcare professionals in making informed decisions, improving patient outcomes, and reducing healthcare costs.
2. What are the main benefits of telemedicine?
Telemedicine offers several benefits, including increased access to healthcare services, reduced costs, and greater convenience for patients. It is particularly beneficial for those living in rural or underserved areas, as well as for individuals with mobility limitations.
3. How will wearable technology shape the future of healthcare?
Wearable devices will continue to play a crucial role in empowering individuals to monitor their health, track their progress, and identify potential health issues early. This data can be used to personalize healthcare recommendations, improve patient engagement, and drive innovation in healthcare.
4. What are the challenges of implementing big data in healthcare?
Implementing big data in healthcare presents several challenges, including data security, privacy concerns, interoperability issues, and the need for skilled data analysts. Overcoming these challenges is essential for realizing the full potential of big data in healthcare.
5. What are the ethical considerations of personalized medicine?
Personalized medicine raises ethical considerations, including the potential for genetic discrimination, access to testing and treatment, and the responsible use of genetic information. It is crucial to address these ethical concerns to ensure that personalized medicine benefits all individuals equitably.
6. How can blockchain improve data security in healthcare?
Blockchain technology offers a secure and tamper-proof platform for storing and sharing patient health records, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. It can also enhance data integrity and transparency in healthcare systems.
7. What are the limitations of digital health apps?
While digital health apps offer numerous benefits, they also have limitations. These include the potential for inaccurate information, privacy concerns, and the need for reliable internet access. It is essential to use reputable apps and to be aware of their limitations.
8. What are the key factors driving the adoption of value-based care?
The adoption of value-based care is driven by several factors, including the rising cost of healthcare, the need to improve patient outcomes, and the growing emphasis on patient engagement. It is a shift towards a more sustainable and patient-centered healthcare system.
Tips
1. Embrace Technology: Healthcare professionals should stay informed about the latest technological advancements and explore how they can be integrated into their practice to enhance patient care.
2. Focus on Patient Engagement: Healthcare providers should empower patients to take an active role in managing their health by providing them with access to information, tools, and support.
3. Promote Data Security and Privacy: Healthcare organizations should prioritize data security and privacy by implementing robust measures to protect patient information and comply with relevant regulations.
4. Invest in Workforce Development: Healthcare organizations should invest in training and development programs to ensure that their workforce is equipped with the skills and knowledge needed to navigate the evolving healthcare landscape.
5. Foster Collaboration and Innovation: Healthcare providers should collaborate with other stakeholders, including technology companies, researchers, and policymakers, to drive innovation and improve healthcare outcomes.
Conclusion
The healthcare industry is on the cusp of significant transformation as technological advancements, changing demographics, and evolving patient expectations reshape the medical landscape. The trends discussed in this article highlight the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead, emphasizing the need for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and industry leaders to embrace innovation, prioritize patient-centered care, and work collaboratively to create a more efficient, effective, and equitable healthcare system for all.
The future of healthcare is bright, but it requires a concerted effort to harness the power of technology, data, and innovation to improve patient outcomes and create a more sustainable and equitable healthcare system for all.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Future of Healthcare: Trends Shaping the Medical Landscape by 2025. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!