Understanding Periodic Trends and Reactivity: A Glimpse into the Future of Chemistry
Understanding Periodic Trends and Reactivity: A Glimpse into the Future of Chemistry
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Periodic Trends and Reactivity: A Glimpse into the Future of Chemistry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Understanding Periodic Trends and Reactivity: A Glimpse into the Future of Chemistry
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Periodic Trends and Reactivity: A Glimpse into the Future of Chemistry
- 3.1 The Periodic Trends: A Foundation for Understanding Reactivity
- 3.2 Beyond Basic Trends: Factors Influencing Reactivity
- 3.3 Periodic Trends Reactivity 2025: A Look Ahead
- 3.4 Related Searches:
- 3.5 FAQs:
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding Periodic Trends and Reactivity:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Understanding Periodic Trends and Reactivity: A Glimpse into the Future of Chemistry
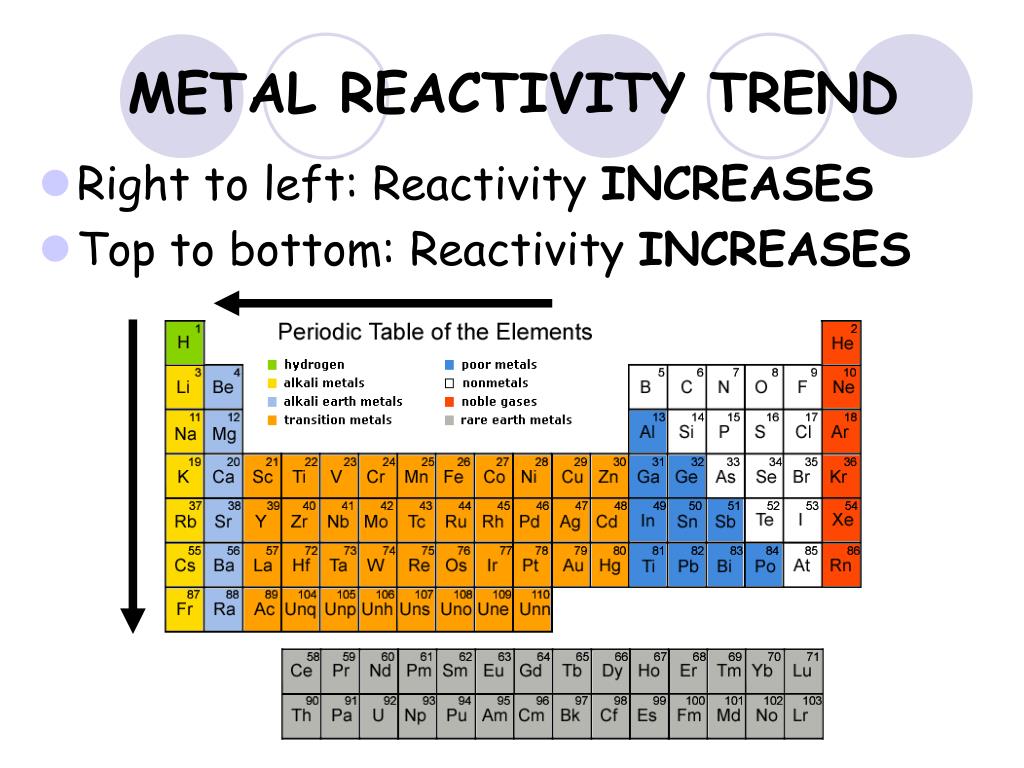
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, provides a systematic organization of elements based on their atomic structure and properties. Within this framework, periodic trends emerge, revealing predictable patterns in how elements behave. One of the most crucial and fascinating aspects of these trends is their influence on reactivity, the tendency of an element to undergo chemical reactions.
Reactivity is a fundamental concept in chemistry, shaping the formation of compounds, the design of materials, and the development of new technologies. As we delve deeper into the realm of chemistry, understanding how reactivity is governed by periodic trends becomes paramount.
The Periodic Trends: A Foundation for Understanding Reactivity
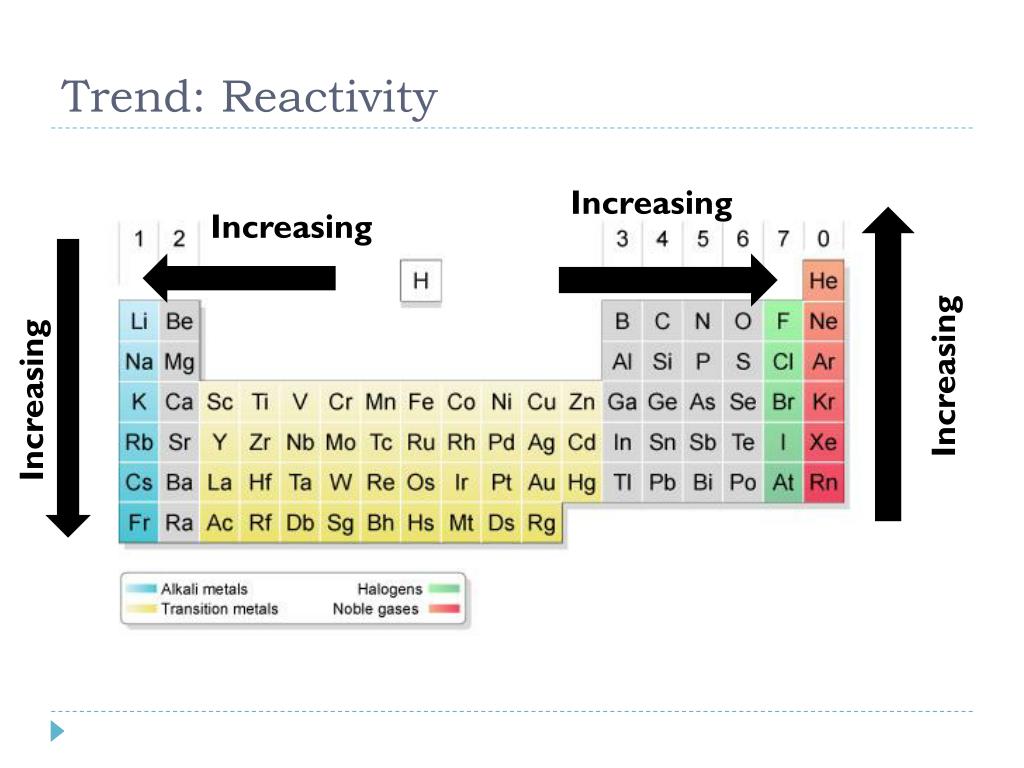
The periodic table is structured in a way that reflects the underlying principles governing atomic behavior. Key periodic trends directly impact reactivity:
- Electronegativity: This trend describes an atom’s tendency to attract electrons in a chemical bond. Electronegativity increases from left to right across a period and decreases down a group. Elements with high electronegativity tend to gain electrons, forming anions, while those with low electronegativity tend to lose electrons, forming cations.
- Ionization Energy: The energy required to remove an electron from an atom in its gaseous state is known as ionization energy. This value increases across a period and decreases down a group. Elements with high ionization energy are less likely to lose electrons, making them less reactive in terms of forming cations.
- Electron Affinity: The change in energy when an electron is added to a neutral atom in its gaseous state is called electron affinity. This value generally increases across a period and decreases down a group. Elements with high electron affinity readily gain electrons, making them more reactive in forming anions.
- Atomic Radius: The size of an atom, measured as its atomic radius, decreases across a period and increases down a group. Smaller atoms tend to have a stronger attraction for electrons, making them more reactive.
These periodic trends work in concert to determine the reactivity of elements. For example, elements in Group 1 (alkali metals) have low ionization energies and low electronegativity, making them highly reactive in losing electrons to form cations. Conversely, elements in Group 17 (halogens) have high electronegativity and high electron affinity, readily gaining electrons to form anions.
Beyond Basic Trends: Factors Influencing Reactivity
While periodic trends provide a fundamental framework, several additional factors can influence reactivity:
- Nuclear Charge: The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, known as its atomic number, influences the strength of its attraction for electrons. A higher nuclear charge leads to stronger attraction, affecting reactivity.
- Electron Shielding: The core electrons in an atom shield the valence electrons from the full pull of the nucleus. This shielding effect reduces the attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons, influencing reactivity.
- Electron Configuration: The specific arrangement of electrons in an atom’s orbitals dictates its chemical behavior. Elements with similar electron configurations often exhibit similar reactivity.
- Oxidation State: The oxidation state of an element indicates its relative charge in a compound. Different oxidation states can lead to varying reactivity patterns.
Periodic Trends Reactivity 2025: A Look Ahead
The year 2025 is just around the corner, and the field of chemistry continues to evolve at a rapid pace. Understanding periodic trends reactivity will be critical in shaping future advancements in various fields:
- Materials Science: Understanding how reactivity changes with atomic structure will enable the design of novel materials with specific properties, such as strength, conductivity, and heat resistance.
- Catalysis: The development of efficient catalysts for chemical reactions relies heavily on understanding the reactivity of different elements. By manipulating periodic trends, scientists can create catalysts with enhanced activity and selectivity.
- Energy Storage: The search for efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions hinges on the development of new battery technologies. Understanding the reactivity of elements involved in battery chemistry is crucial for designing batteries with higher capacity and longevity.
- Environmental Chemistry: Addressing environmental challenges, such as pollution and climate change, requires a deep understanding of chemical reactions and their influence on the environment. Periodic trends reactivity plays a vital role in developing solutions for environmental remediation and sustainable practices.
Related Searches:
1. Periodic Trends and Chemical Bonding: The relationship between periodic trends and the types of chemical bonds (ionic, covalent, metallic) formed between elements is a crucial aspect of understanding reactivity.
2. Periodic Trends and Chemical Reactions: How periodic trends dictate the types of reactions elements participate in, including oxidation-reduction reactions, acid-base reactions, and precipitation reactions.
3. Periodic Trends and Properties of Compounds: Understanding how periodic trends influence the properties of compounds, such as melting point, boiling point, and solubility, is essential for predicting their behavior and applications.
4. Periodic Trends and Reaction Rates: The rate at which a chemical reaction proceeds is influenced by the reactivity of the elements involved. Periodic trends can help predict and control reaction rates.
5. Periodic Trends and Chemical Equilibrium: The concept of chemical equilibrium, where the rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal, is influenced by the reactivity of the species involved. Understanding periodic trends can aid in predicting and manipulating equilibrium positions.
6. Periodic Trends and Organic Chemistry: The reactivity of organic molecules is heavily influenced by the functional groups present. Periodic trends play a role in understanding the reactivity of these functional groups.
7. Periodic Trends and Biochemistry: The reactivity of biomolecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, is governed by the underlying chemical properties of the atoms involved. Understanding periodic trends helps unravel the complex interactions within biological systems.
8. Periodic Trends and Nanotechnology: The design and development of nanomaterials often rely on manipulating the properties of elements at the nanoscale. Periodic trends provide insights into the reactivity and behavior of elements in these tiny structures.
FAQs:
1. What is the significance of periodic trends in reactivity?
Periodic trends provide a fundamental framework for understanding how elements behave in chemical reactions. They allow us to predict the reactivity of elements and design new materials and technologies.
2. How do periodic trends impact the formation of compounds?
Periodic trends influence the types of bonds formed between elements, the stability of compounds, and the properties of the resulting substances.
3. Can periodic trends be used to predict the outcome of chemical reactions?
While not always completely predictive, periodic trends offer valuable insights into the likelihood of certain reactions occurring and the products that might form.
4. How do periodic trends affect the development of new technologies?
Understanding periodic trends allows scientists to tailor the properties of materials for specific applications, leading to advancements in various fields, including energy, medicine, and electronics.
5. Are there any exceptions to periodic trends?
While periodic trends generally hold true, there are some exceptions due to factors like electron configuration and the presence of transition metals.
6. How can I learn more about periodic trends and reactivity?
Numerous resources are available, including textbooks, online courses, and scientific journals. Consulting with a chemistry instructor or researcher can also provide valuable guidance.
Tips for Understanding Periodic Trends and Reactivity:
- Visualize the periodic table: Familiarize yourself with the layout of the periodic table and the positions of different elements.
- Focus on key trends: Understand the trends in electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, and atomic radius.
- Relate trends to reactivity: Connect the periodic trends to the tendency of elements to form ions, participate in reactions, and influence the properties of compounds.
- Practice applying the concepts: Solve problems and answer questions related to periodic trends and reactivity to solidify your understanding.
- Explore real-world applications: Connect your knowledge to real-world examples, such as the use of alkali metals in batteries or the role of halogens in disinfectants.
Conclusion:
Understanding periodic trends and their influence on reactivity is crucial for anyone studying or working in chemistry. These trends provide a foundation for understanding the behavior of elements, predicting the outcomes of reactions, and designing new materials and technologies. As the field of chemistry continues to advance, the importance of periodic trends reactivity will only grow, shaping the future of science and technology.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)

.PNG)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Periodic Trends and Reactivity: A Glimpse into the Future of Chemistry. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!