Understanding the Climate Crossroads: A Deep Dive into the Warming Trends of 2025
Understanding the Climate Crossroads: A Deep Dive into the Warming Trends of 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Climate Crossroads: A Deep Dive into the Warming Trends of 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Understanding the Climate Crossroads: A Deep Dive into the Warming Trends of 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Climate Crossroads: A Deep Dive into the Warming Trends of 2025
- 3.1 Understanding the Trajectory of Warming Trends
- 3.2 The Looming Threat of Climate Tipping Points
- 3.3 The Urgency of Adaptation and Mitigation
- 3.4 The Importance of Global Collaboration
- 3.5 Related Searches:
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
- 3.7 Tips for Addressing the Warming Trends of 2025:
- 3.8 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Climate Crossroads: A Deep Dive into the Warming Trends of 2025

The year 2025 is a pivotal moment in the ongoing narrative of climate change. It serves as a critical juncture, marking a significant shift in the Earth’s warming trends and their potential consequences. While the term "warming trends crossfire 2025" itself is not a widely used term, it encapsulates the convergence of several key factors:
- Accelerated Warming: Global temperatures are rising at an alarming rate, surpassing previous projections.
- Climate Tipping Points: The Earth’s systems are approaching thresholds beyond which irreversible changes may occur, leading to cascading effects on the planet’s climate.
- Human Impact Intensification: Human activities continue to drive climate change, with greenhouse gas emissions reaching record highs.
- Adaptation and Mitigation Challenges: The world faces mounting pressure to adapt to the changing climate and mitigate further warming, requiring significant global collaboration and innovation.
This convergence of factors creates a complex scenario where the world’s climate is rapidly evolving, demanding a comprehensive understanding of the underlying trends and their potential implications.
Understanding the Trajectory of Warming Trends
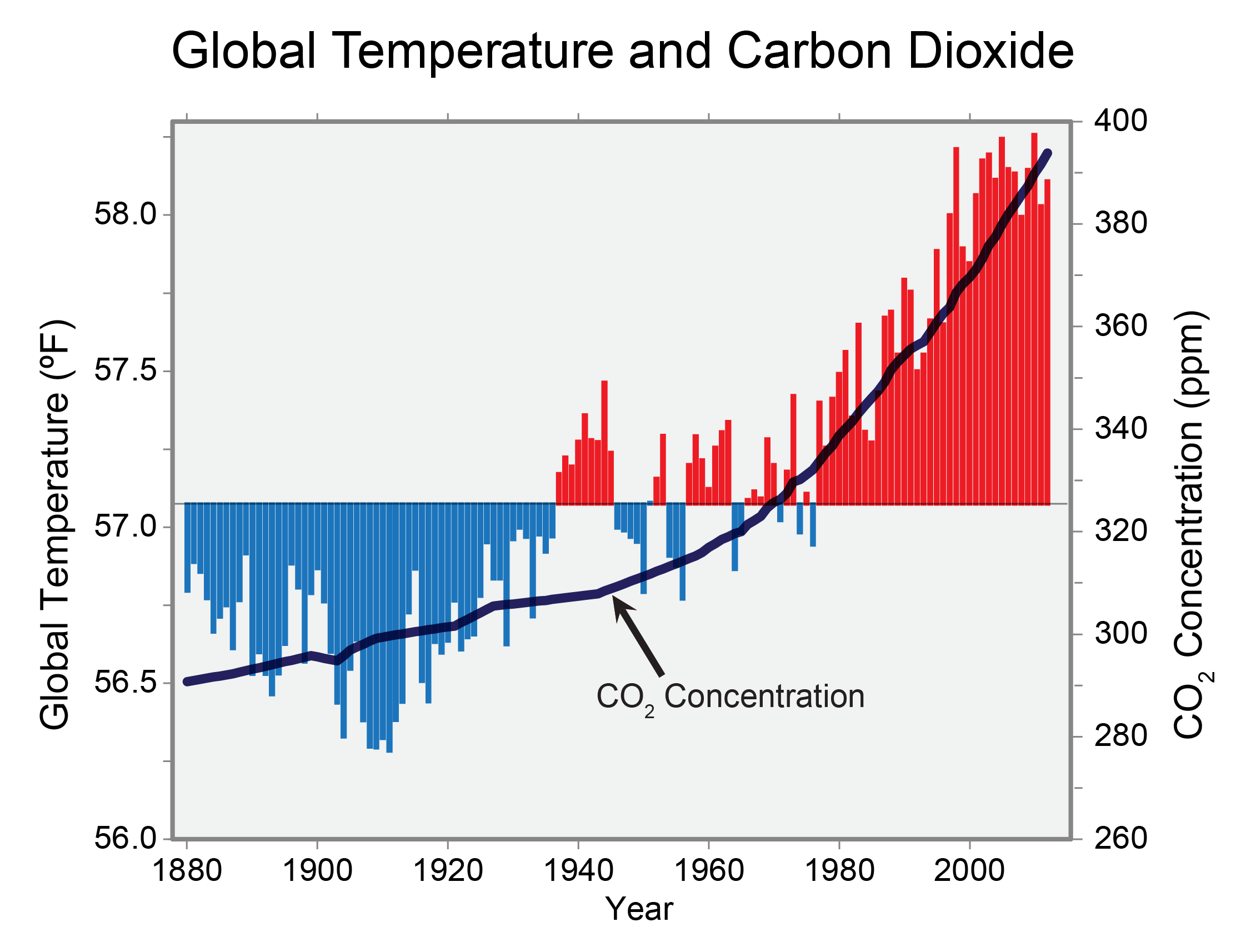
The Earth’s climate has always fluctuated, but the current warming trend is unprecedented in its speed and magnitude. Since the pre-industrial era, global temperatures have risen by approximately 1 degree Celsius, and projections indicate a further increase of 1.5 to 2 degrees Celsius by 2050. This warming trend is primarily driven by human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Key Drivers of the Accelerated Warming Trend:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to a gradual increase in global temperatures.
- Deforestation: Forests act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Deforestation reduces this capacity, further exacerbating the warming trend.
- Industrialization and Urbanization: Industrial processes and urban sprawl contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, driving climate change.
- Agriculture and Land Use: Agricultural practices, particularly livestock farming and deforestation for agricultural expansion, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and exacerbate the warming trend.
These factors are interconnected and amplify each other, creating a complex feedback loop that accelerates the warming trend.
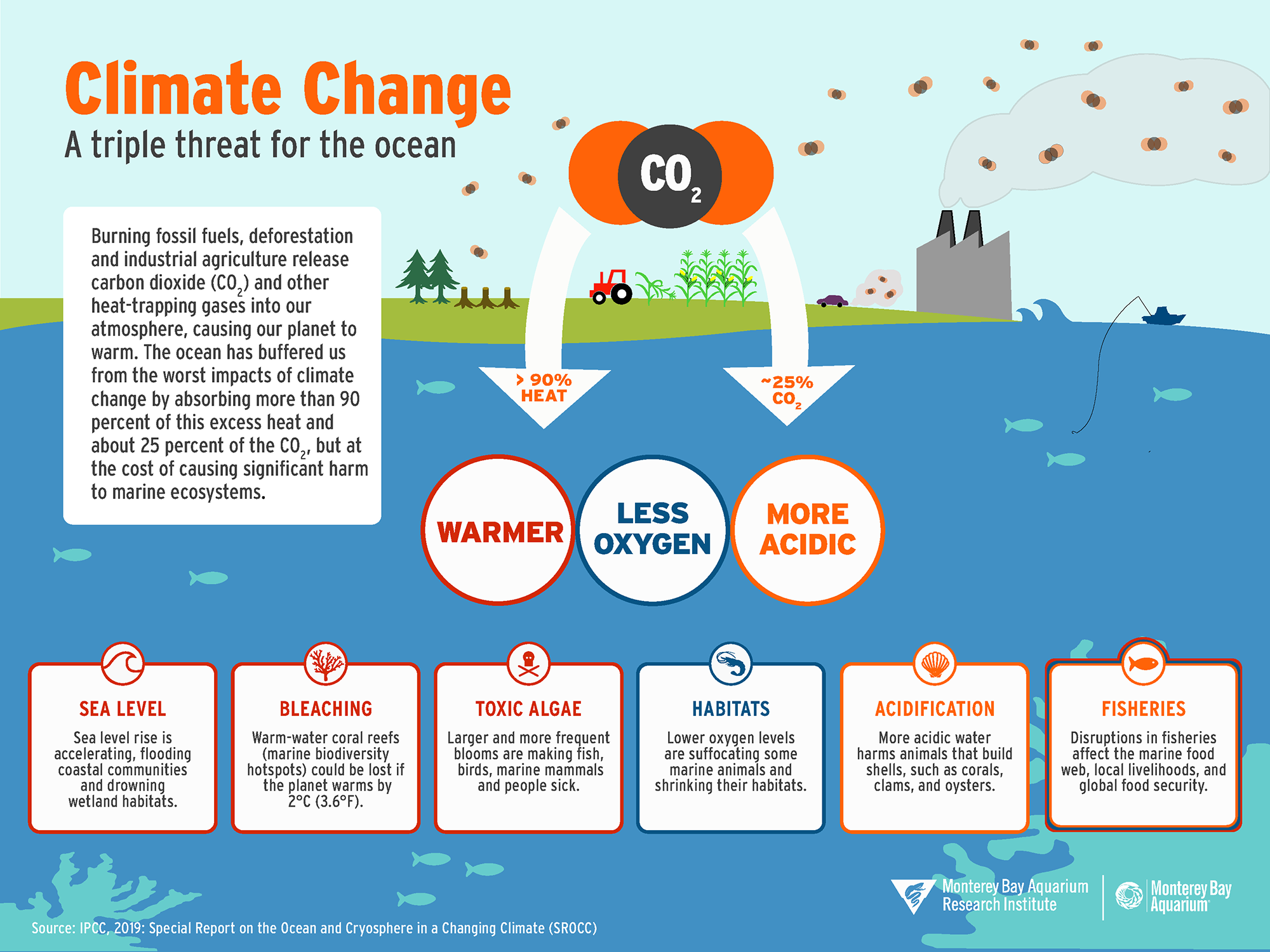
The Looming Threat of Climate Tipping Points
Climate tipping points represent thresholds beyond which the Earth’s climate system experiences irreversible changes. These changes can cascade across different systems, leading to significant and potentially catastrophic consequences.
Some of the key climate tipping points include:
- Melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet: The melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet could raise global sea levels by several meters, displacing millions of people and causing widespread coastal flooding.
- Amazon Rainforest Dieback: The Amazon rainforest, a vital carbon sink, could experience dieback due to drought and deforestation, releasing massive amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and accelerating warming.
- Coral Reef Bleaching: Rising ocean temperatures and acidification are leading to widespread coral bleaching, threatening the survival of these vital ecosystems and impacting marine biodiversity.
- Permafrost Thaw: The thawing of permafrost releases methane, a powerful greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere, further accelerating the warming trend.
These tipping points are interconnected, and the crossing of one threshold can trigger others, creating a domino effect that could dramatically alter the Earth’s climate system.
The Urgency of Adaptation and Mitigation
The warming trends of 2025 necessitate a comprehensive and coordinated global response. This response must encompass two key strategies: adaptation and mitigation.
Adaptation Strategies:
- Infrastructure Resilience: Adapting infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events, such as sea-level rise, floods, and droughts.
- Water Management: Developing strategies to manage water resources effectively in the face of changing precipitation patterns and increased water stress.
- Food Security: Ensuring food security by adapting agricultural practices to changing climate conditions and developing drought-resistant crops.
- Public Health: Protecting public health from the impacts of climate change, such as heat waves, air pollution, and the spread of infectious diseases.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Transition to Renewable Energy: Shifting away from fossil fuels and investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal power.
- Energy Efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industrial processes to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Developing technologies to capture and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere or industrial processes.
- Forest Conservation and Reforestation: Protecting existing forests and promoting reforestation to increase carbon sinks and mitigate climate change.
The Importance of Global Collaboration
Addressing the warming trends of 2025 requires a collective effort from all nations. International cooperation is crucial to sharing knowledge, developing sustainable solutions, and mobilizing resources.
Key International Agreements:
- Paris Agreement: An international agreement aimed at limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial levels.
- UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC): A framework for international cooperation on climate change, providing a platform for negotiations and agreements.
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): A scientific body that provides comprehensive assessments of climate change science, impacts, and adaptation and mitigation options.
Related Searches:
1. Climate Change Impacts: This search explores the specific impacts of climate change on various aspects of life, including human health, ecosystems, agriculture, and water resources.
2. Climate Change Projections: This search delves into future climate projections, including temperature increases, sea-level rise, and changes in precipitation patterns.
3. Climate Change Mitigation: This search focuses on strategies and technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
4. Climate Change Adaptation: This search explores strategies for adapting to the impacts of climate change, such as building resilience and managing water resources.
5. Climate Change Solutions: This search examines a wide range of solutions to address climate change, including technological innovations, policy changes, and behavioral shifts.
6. Climate Change Denial: This search explores the arguments and evidence against the scientific consensus on climate change, as well as the motivations behind denial.
7. Climate Change Education: This search focuses on the importance of climate change education and the role of education in raising awareness, promoting understanding, and fostering action.
8. Climate Change Activism: This search examines the role of activism in driving climate change action, including protests, campaigns, and advocacy efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What is the scientific consensus on climate change?
The scientific consensus on climate change is overwhelming, with over 97% of climate scientists agreeing that human activities are the primary cause of the current warming trend. This consensus is based on decades of scientific research and observations.
2. What are the potential consequences of climate change?
The potential consequences of climate change are vast and varied, including rising sea levels, more frequent and intense extreme weather events, changes in precipitation patterns, impacts on ecosystems and biodiversity, and threats to human health and food security.
3. What can I do to address climate change?
Individuals can make a difference by reducing their carbon footprint, supporting policies that address climate change, and raising awareness about the issue.
4. What are the economic implications of climate change?
Climate change has significant economic implications, including costs associated with damage from extreme weather events, disruptions to supply chains, and the need to adapt to changing conditions.
5. What is the role of technology in addressing climate change?
Technology plays a crucial role in addressing climate change, particularly in developing renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and developing carbon capture and storage technologies.
Tips for Addressing the Warming Trends of 2025:
- Reduce your carbon footprint: Make conscious choices to reduce your emissions, such as using public transportation, cycling, or walking instead of driving, reducing energy consumption at home, and adopting a more sustainable lifestyle.
- Support climate-friendly policies: Advocate for policies that promote renewable energy, energy efficiency, and carbon pricing.
- Invest in sustainable solutions: Consider investing in companies and projects that are working to address climate change.
- Educate yourself and others: Stay informed about climate change and share your knowledge with others.
- Get involved in activism: Join organizations working to address climate change and participate in campaigns and protests.
Conclusion:
The warming trends of 2025 present a critical juncture for the planet. The convergence of accelerated warming, climate tipping points, and human impact intensification demands a comprehensive and coordinated global response. Adaptation and mitigation strategies are essential to navigate this complex challenge, and global collaboration is crucial for achieving a sustainable future. By understanding the science, taking action, and advocating for change, we can work together to mitigate the impacts of climate change and protect our planet for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Climate Crossroads: A Deep Dive into the Warming Trends of 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!